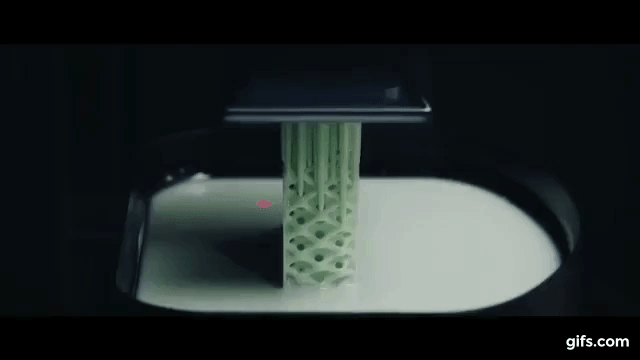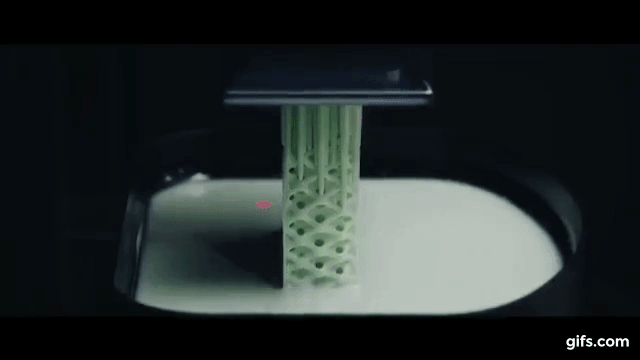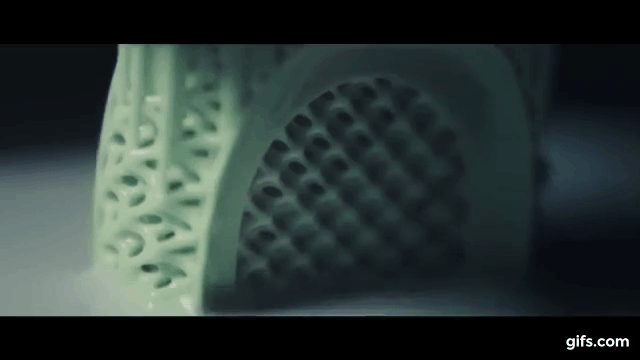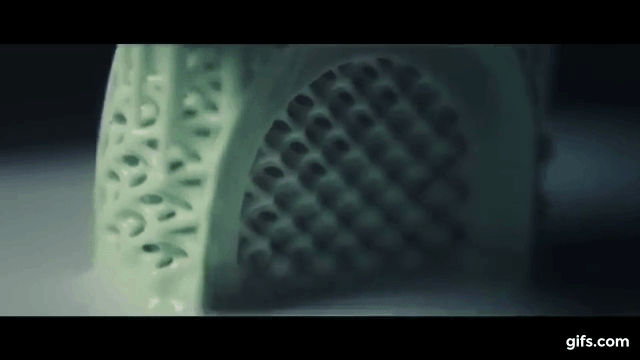
3 D Printing Organs. It is extremely broad both geographically and in. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. 3d printed bone replacements have also been successfully transplanted, but living tissue is the next big step for this ground breaking technology. In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. What's the current status of 3d printing organs? »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. They're developing 3d printers that can also save and change lives by printing out functional human organs. Sure, 3d printers that can spit out chocolates, create shoes, handcraft cars and help astronauts sound fun and magical, but a lot of scientists are working to make models that aren't just fun. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Read our guide to 3d bioprinting, 3d printed organs & medical 3d printing to get an overview. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts.
3 D Printing Organs , 3D Printed Organs, Prosthetics, Bionic Ears And Plastic Foetuses Are Changing Medicine And Healthcare.
United Therapeutics Partners With 3 D Printer To Make Human Organs. 3d printed bone replacements have also been successfully transplanted, but living tissue is the next big step for this ground breaking technology. It is extremely broad both geographically and in. Read our guide to 3d bioprinting, 3d printed organs & medical 3d printing to get an overview. Sure, 3d printers that can spit out chocolates, create shoes, handcraft cars and help astronauts sound fun and magical, but a lot of scientists are working to make models that aren't just fun. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. They're developing 3d printers that can also save and change lives by printing out functional human organs. What's the current status of 3d printing organs? In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here.

How to print solid organs?
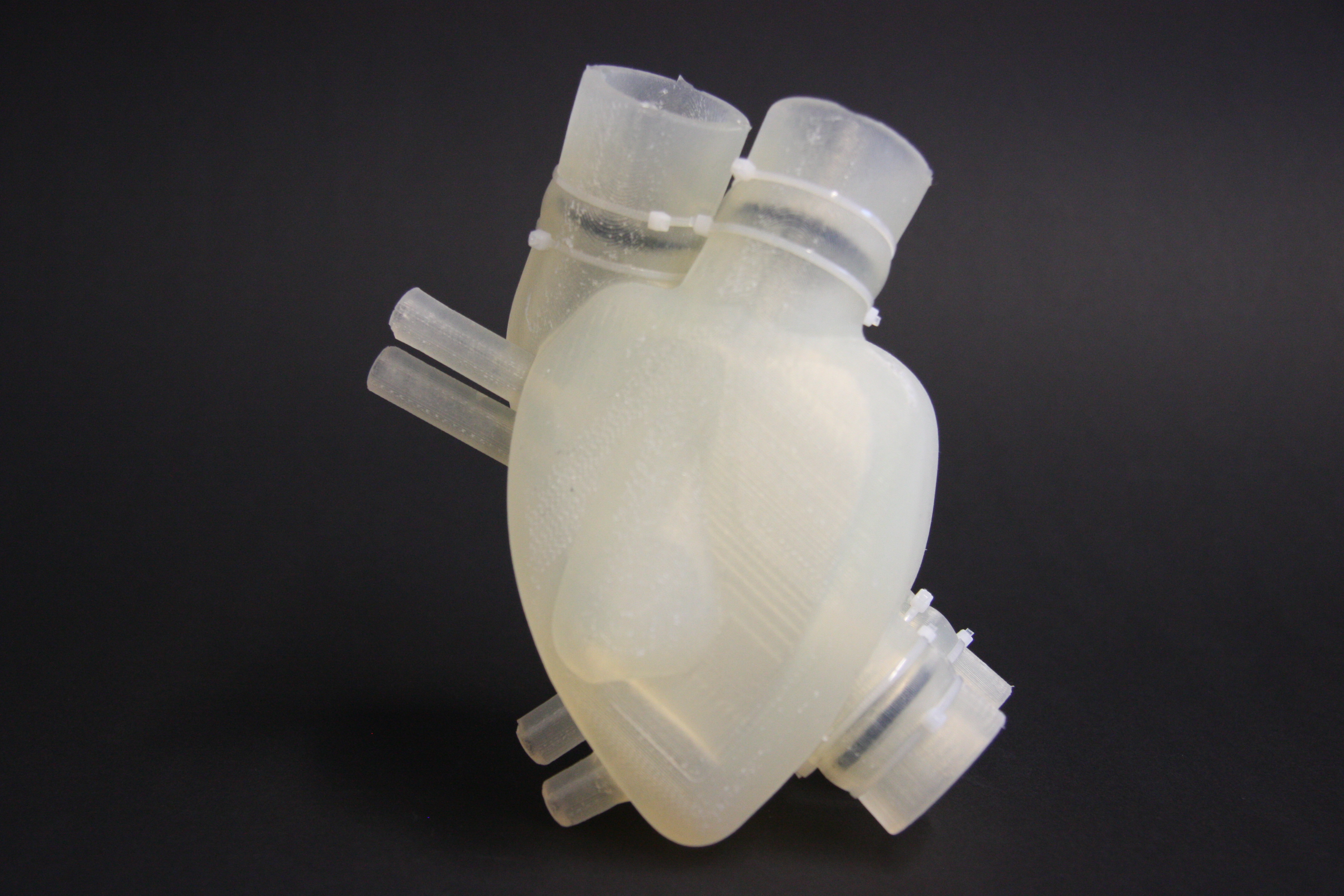
In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. Researchers try to develop 3d printing of body parts. It is hoped one day the technology could make it possible to print replacement body parts or organs. Creating these blood vessel trees, which branch from large arteries into the tiniest vessels. It's going to 3d print replacement human organs—even a fully functional human heart. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; Perfectly fabricating organs mean fewer chances of failure or rejection. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. There's considerable excitement that 3d printing technology might one day allow scientists to produce fully functional replacement organs from one's own cells. 3d printing may be able to print the seed of a more complicated organ, building the outline of such a thing and letting the cells develop the necessary structures and. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. To create a solid organ, researchers need a way to promote the growth of blood vessels so that every cell in the organ receives the oxygen and nutrients and it can eliminate waste. An artificial prostate fitted with a soft sensor. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. How to print an organ. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. You might be surprised to hear that the process for printing organs and other living tissue is incredibly. Read our guide to 3d bioprinting, 3d printed organs & medical 3d printing to get an overview. These dummy organs could one day improve your chances of surviving surgery, by allowing doctors to plan and practice a lifesaving procedure on a realistic replica before putting you to the scalpel. In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. What's the current status of 3d printing organs?
Microgel Supports 3d Printing Technique That Builds Organs Out Of Stem Cells Research Chemistry World : An Artificial Prostate Fitted With A Soft Sensor.
3d Bioprinting Is This The Future Of Organ Transplantation. 3d printed bone replacements have also been successfully transplanted, but living tissue is the next big step for this ground breaking technology. What's the current status of 3d printing organs? Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. It is extremely broad both geographically and in. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. Read our guide to 3d bioprinting, 3d printed organs & medical 3d printing to get an overview. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. They're developing 3d printers that can also save and change lives by printing out functional human organs. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. Sure, 3d printers that can spit out chocolates, create shoes, handcraft cars and help astronauts sound fun and magical, but a lot of scientists are working to make models that aren't just fun.
What You Need To Know About 3d Printed Organs Engadget , There's Considerable Excitement That 3D Printing Technology Might One Day Allow Scientists To Produce Fully Functional Replacement Organs From One's Own Cells.
3d Bioprinting Is This The Future Of Organ Transplantation. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. What's the current status of 3d printing organs? In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. They're developing 3d printers that can also save and change lives by printing out functional human organs. 3d printed bone replacements have also been successfully transplanted, but living tissue is the next big step for this ground breaking technology. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution.
Is 3d Bioprinting The Future Of Tailor Made Medicine 3dnatives : You might be surprised to hear that the process for printing organs and other living tissue is incredibly.
Silicon Valley Startup 3d Printing Human Organs To Save Lives. It is extremely broad both geographically and in. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. What's the current status of 3d printing organs? Sure, 3d printers that can spit out chocolates, create shoes, handcraft cars and help astronauts sound fun and magical, but a lot of scientists are working to make models that aren't just fun. In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. They're developing 3d printers that can also save and change lives by printing out functional human organs. Read our guide to 3d bioprinting, 3d printed organs & medical 3d printing to get an overview. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. 3d printed bone replacements have also been successfully transplanted, but living tissue is the next big step for this ground breaking technology.
What You Need To Know About 3d Printed Organs Engadget - What They Have Learnt So Far Is That The Fabrication Of Inanimate Objects Is Easier Than Living Body Parts.
Is 3d Bioprinting The Future Of Tailor Made Medicine 3dnatives. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. It is extremely broad both geographically and in. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Sure, 3d printers that can spit out chocolates, create shoes, handcraft cars and help astronauts sound fun and magical, but a lot of scientists are working to make models that aren't just fun. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. What's the current status of 3d printing organs? What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. Read our guide to 3d bioprinting, 3d printed organs & medical 3d printing to get an overview. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. They're developing 3d printers that can also save and change lives by printing out functional human organs. 3d printed bone replacements have also been successfully transplanted, but living tissue is the next big step for this ground breaking technology.
New Diy 3 D Bioprinter To Create Living Human Organs Longevityfacts . While There's Still A Lot To Learn, This Video Shows Just Some Of The Amazing Progress That's Now Being Made.
Doctor 3d Prints Tissues Organs Positive For Fda Approval The Merkle News. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. They're developing 3d printers that can also save and change lives by printing out functional human organs. It is extremely broad both geographically and in. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. Read our guide to 3d bioprinting, 3d printed organs & medical 3d printing to get an overview. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. Sure, 3d printers that can spit out chocolates, create shoes, handcraft cars and help astronauts sound fun and magical, but a lot of scientists are working to make models that aren't just fun. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. 3d printed bone replacements have also been successfully transplanted, but living tissue is the next big step for this ground breaking technology. What's the current status of 3d printing organs?
Organ Printing Wikipedia . Recent Advances Have Enabled 3D Printing Of Biocompatible Materials, Cells And Supporting Components Into Complex 3D Functional Living Tissues.
Scientists Can Now 3d Print Functional Organs Youtube. In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. It is extremely broad both geographically and in. They're developing 3d printers that can also save and change lives by printing out functional human organs. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. Read our guide to 3d bioprinting, 3d printed organs & medical 3d printing to get an overview. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. What's the current status of 3d printing organs? 3d printed bone replacements have also been successfully transplanted, but living tissue is the next big step for this ground breaking technology. Sure, 3d printers that can spit out chocolates, create shoes, handcraft cars and help astronauts sound fun and magical, but a lot of scientists are working to make models that aren't just fun.
5 Ways 3d Printing Could Totally Change Medicine Futurity . Eventually, However, The Pioneers Of This Technology Believe They Will Be Able To Create Complex Organs, Such As Hearts And Livers, From Scratch.
World S First 3d Printed Heart Could Revolutionize Organ Transplants. What's the current status of 3d printing organs? Read our guide to 3d bioprinting, 3d printed organs & medical 3d printing to get an overview. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. They're developing 3d printers that can also save and change lives by printing out functional human organs. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. It is extremely broad both geographically and in. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. 3d printed bone replacements have also been successfully transplanted, but living tissue is the next big step for this ground breaking technology. Sure, 3d printers that can spit out chocolates, create shoes, handcraft cars and help astronauts sound fun and magical, but a lot of scientists are working to make models that aren't just fun. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced.
The Emerging Industry Of 3d Printed Organs Will Become A Billion Dollar Industry In 10 Years . What's The Current Status Of 3D Printing Organs?
The Emerging Industry Of 3d Printed Organs Will Become A Billion Dollar Industry In 10 Years. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. It is extremely broad both geographically and in. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. They're developing 3d printers that can also save and change lives by printing out functional human organs. Read our guide to 3d bioprinting, 3d printed organs & medical 3d printing to get an overview. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. Sure, 3d printers that can spit out chocolates, create shoes, handcraft cars and help astronauts sound fun and magical, but a lot of scientists are working to make models that aren't just fun. 3d printed bone replacements have also been successfully transplanted, but living tissue is the next big step for this ground breaking technology. What's the current status of 3d printing organs? In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body.
The Next Frontier In 3 D Printing Human Organs Cnn , How To Print An Organ.
What Is The Future Of 3d Printed Organs 2020 Update. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. 3d printed bone replacements have also been successfully transplanted, but living tissue is the next big step for this ground breaking technology. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. Read our guide to 3d bioprinting, 3d printed organs & medical 3d printing to get an overview. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. Sure, 3d printers that can spit out chocolates, create shoes, handcraft cars and help astronauts sound fun and magical, but a lot of scientists are working to make models that aren't just fun. It is extremely broad both geographically and in. What's the current status of 3d printing organs? They're developing 3d printers that can also save and change lives by printing out functional human organs. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body.
3d Printed Organs Nearing Clinical Trials Asme : 3D Printed Bone Replacements Have Also Been Successfully Transplanted, But Living Tissue Is The Next Big Step For This Ground Breaking Technology.
3d Printing Organs Changing Surgery For All The Members Of Your Family Navigate The Future. They're developing 3d printers that can also save and change lives by printing out functional human organs. In the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. Sure, 3d printers that can spit out chocolates, create shoes, handcraft cars and help astronauts sound fun and magical, but a lot of scientists are working to make models that aren't just fun. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. The current and ongoing research into 3d bioprinting applications generates huge interest and excitement. What's the current status of 3d printing organs? 3d printed bone replacements have also been successfully transplanted, but living tissue is the next big step for this ground breaking technology. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. It is extremely broad both geographically and in. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. Eventually, however, the pioneers of this technology believe they will be able to create complex organs, such as hearts and livers, from scratch. Read our guide to 3d bioprinting, 3d printed organs & medical 3d printing to get an overview.