3D Bioprinting Process. For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs. Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus. Steps in the bioprinting process are imaging and design, choice of. Figure 1 a typical process for bioprinting 3d tissues. This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. Jump to navigationjump to search. 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems. How does 3d bioprinting work? Bioprinting refers to 3d printers which deposit layers of biomaterial to build complex bodily structures like skin, bones and even corneas.
3D Bioprinting Process , Imaging Of The Damaged Tissue And Its Environment Can Be Used To Guide The Design However, The Requirement.
Scientists 3d Printing In Situ For Tissue Regeneration 3dprint Com The Voice Of 3d Printing Additive Manufacturing. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. Figure 1 a typical process for bioprinting 3d tissues. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together. Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs. Steps in the bioprinting process are imaging and design, choice of. Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. How does 3d bioprinting work? This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems. Bioprinting refers to 3d printers which deposit layers of biomaterial to build complex bodily structures like skin, bones and even corneas. For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. Jump to navigationjump to search.
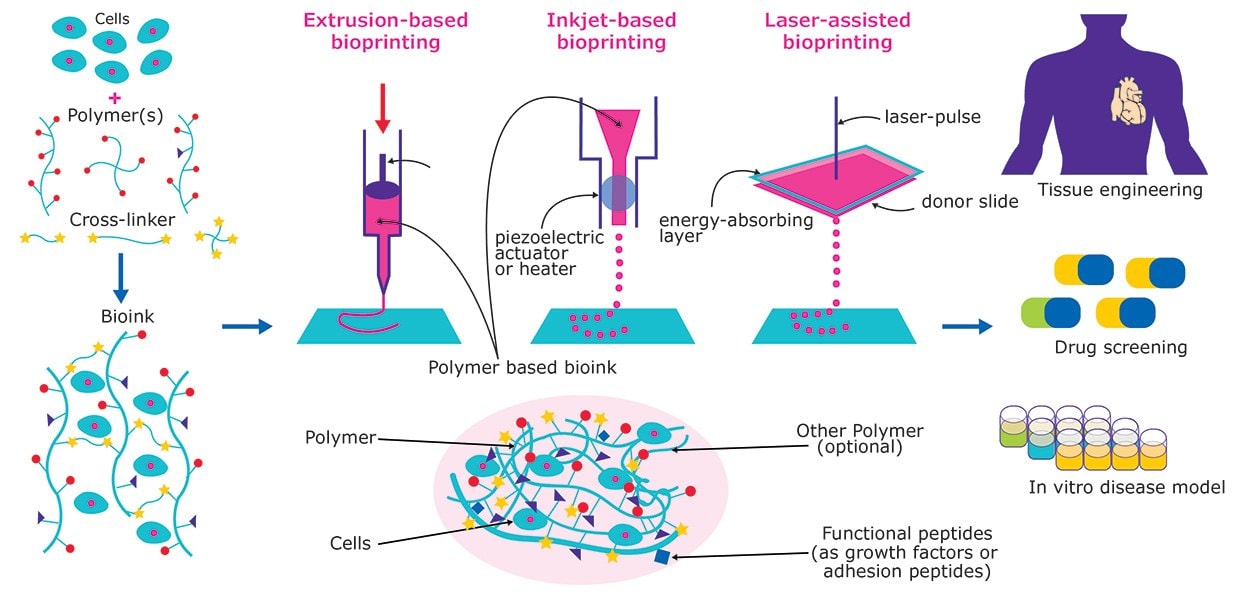
3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems.
Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus. For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. The bioprinting process has many similarities with the 3d printing process. 3d bioprinting of tissues and organs will find application in tissue engineering, research, drug discovery and toxicology. Bioprinting of 3d convoluted renal proximal tubules on perfusable chips. Our bioprinting process starts with the identification of key architectural and compositional elements of a target tissue, and the creation of a design that can be utilized by a bioprinter to generate that tissue in the laboratory environment. Steps in the bioprinting process are imaging and design, choice of. Like in other types of 3d printing, layers of material are. Jump to navigationjump to search. Russia russia's leading bioprinting firm, 3d bioprinting solutions aims to 3d print multiple human organs. Figure 1 a typical process for bioprinting 3d tissues. 3d bioprinting can be defined in a variety of ways, and each definition includes and excludes large swathes of key biotechnology markets. Technologies and considerations relevant to the 3d bioprinting process, such as software, bioink (including cell selection, growth factors, and scaffold. Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together. Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. How does 3d bioprinting work? Aspect biosystems is a canadian. 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. The bioink is used to load specialized print cartridges, which are composed of syringes fitted with long extrusion nozzles. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs. Bioprinting refers to 3d printers which deposit layers of biomaterial to build complex bodily structures like skin, bones and even corneas. While scientist already use 3d printing process to create custom implants and prosthesis in polymeric or metal materials. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. The wyss team is also investigating the use of 3d bioprinting to fabricate new versions of the institute's organs on chips devices. Bioprinting is generally divided into the following processing: So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. Living cells in a 3d printer. sciencedaily. The tissue or organ based on the 3d model in the preprocessing stage is printed.
3d And 4d Bioprinting Of The Myocardium Current Approaches Challenges And Future Prospects : Living Cells In A 3D Printer. Sciencedaily.
Linear Banner Of 3d Bioprinting Stock Illustration Illustration Of Cell Bioprinter 121605480. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together. For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs. How does 3d bioprinting work? Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. Steps in the bioprinting process are imaging and design, choice of. Figure 1 a typical process for bioprinting 3d tissues. Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus. Jump to navigationjump to search. This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems. Bioprinting refers to 3d printers which deposit layers of biomaterial to build complex bodily structures like skin, bones and even corneas.
Clinical Perspectives On 3d Bioprinting Paradigms For Regenerative Medicine , Like In Other Types Of 3D Printing, Layers Of Material Are.
Support Bath Enables 3d Printing Of Soft Biomaterials. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together. So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. How does 3d bioprinting work? For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems.
3d Bioprinting A Revolutionary Technology In The Healthcare Industry - Like in other types of 3d printing, layers of material are.
Philly Biotech Scene Biobots And 3d Bioprinting Now Called Allevi Leaders In Pharmaceutical Business Intelligence Lpbi Group. So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs. 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems. Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus. Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. Steps in the bioprinting process are imaging and design, choice of. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. Figure 1 a typical process for bioprinting 3d tissues. Jump to navigationjump to search. This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. How does 3d bioprinting work? For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. Bioprinting refers to 3d printers which deposit layers of biomaterial to build complex bodily structures like skin, bones and even corneas. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together.
Skin Bioprinting The Future Of Burn Wound Reconstruction Burns Trauma Full Text - Like In Other Types Of 3D Printing, Layers Of Material Are.
3d Bioprinting 2018 2028 Technologies Markets Forecasts Idtechex. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together. 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. Jump to navigationjump to search. This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. How does 3d bioprinting work? Bioprinting refers to 3d printers which deposit layers of biomaterial to build complex bodily structures like skin, bones and even corneas. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. Steps in the bioprinting process are imaging and design, choice of. Figure 1 a typical process for bioprinting 3d tissues. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs. Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus.
The Emerging Role Of Microfluidics In Multi Material 3d Bioprinting Lab On A Chip Rsc Publishing : Steps In The Bioprinting Process Are Imaging And Design, Choice Of.
Aspect Biosystems The Bioprinting Process Youtube. So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. Steps in the bioprinting process are imaging and design, choice of. 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems. Figure 1 a typical process for bioprinting 3d tissues. Bioprinting refers to 3d printers which deposit layers of biomaterial to build complex bodily structures like skin, bones and even corneas. This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs. Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. Jump to navigationjump to search. Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together. How does 3d bioprinting work?
What Is Bioprinting Science Abc , Imaging Of The Damaged Tissue And Its Environment Can Be Used To Guide The Design However, The Requirement.
3d Bioprinting Process Vertical Section Side View Of Various Download Scientific Diagram. Figure 1 a typical process for bioprinting 3d tissues. Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. How does 3d bioprinting work? Jump to navigationjump to search. Bioprinting refers to 3d printers which deposit layers of biomaterial to build complex bodily structures like skin, bones and even corneas. 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus. For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. Steps in the bioprinting process are imaging and design, choice of. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs.
Scheme Showing The Bioprinting Process A Diagram Of The 3d Download Scientific Diagram , Technologies And Considerations Relevant To The 3D Bioprinting Process, Such As Software, Bioink (Including Cell Selection, Growth Factors, And Scaffold.
3d Bioprinting Of Tissues And Organs Nature Biotechnology. Steps in the bioprinting process are imaging and design, choice of. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. Bioprinting refers to 3d printers which deposit layers of biomaterial to build complex bodily structures like skin, bones and even corneas. 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems. Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus. Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs. This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. How does 3d bioprinting work? For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together. Figure 1 a typical process for bioprinting 3d tissues. Jump to navigationjump to search.
3d Bioprinting Technologies For Tissue Engineering A Mini Review : So Far It's Only Been Tested On Sheep, But Its Developers.
Researchers 3d Bioprint The First Ears Made From Childen S Own Cells All3dp. 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems. How does 3d bioprinting work? Jump to navigationjump to search. Figure 1 a typical process for bioprinting 3d tissues. So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs. This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus. Steps in the bioprinting process are imaging and design, choice of. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. Bioprinting refers to 3d printers which deposit layers of biomaterial to build complex bodily structures like skin, bones and even corneas.
Bioinks For 3d Bioprinting An Overview Biomaterials Science Rsc Publishing : Aspect Biosystems Is A Canadian.
Development Of 3d Bioprinting From Printing Methods To Biomedical Applications Sciencedirect. So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. Figure 1 a typical process for bioprinting 3d tissues. How does 3d bioprinting work? Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus. Jump to navigationjump to search. This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. Bioprinting refers to 3d printers which deposit layers of biomaterial to build complex bodily structures like skin, bones and even corneas. 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. Steps in the bioprinting process are imaging and design, choice of.
3d Bioprinting Stem Cell Derived Tissues Springerlink : Bioprinting Of 3D Convoluted Renal Proximal Tubules On Perfusable Chips.
The Emerging Role Of Microfluidics In Multi Material 3d Bioprinting Lab On A Chip Rsc Publishing. How does 3d bioprinting work? 3d bioprinting is a form of additive manufacturing that uses cells and other materials as inks to print living structures which mimic natural systems. So far it's only been tested on sheep, but its developers. Organovo thoroughly explains the 3d bioprinting process in this video. Jump to navigationjump to search. Imaging of the damaged tissue and its environment can be used to guide the design however, the requirement. Much like 3d printed bones, the cartilage undergoes a process of growth and development within the body. Figure 1 a typical process for bioprinting 3d tissues. This innovative bioprinting approach can be modified to create various vascularized 3d tissues for regenerative medicine and drug testing endeavors. Steps in the bioprinting process are imaging and design, choice of. The tissue engineering field has emerged as a solution to the shortages of organ and transplantation needs. Collagen is another material used to fuse the cells together. Bioprinting refers to 3d printers which deposit layers of biomaterial to build complex bodily structures like skin, bones and even corneas. For crosslinking often slows the bioprinting process and involves. Home documents assignments wiki schedule wiki pages course syllabus.


