3D Printer Used For Organs. The device is already capable of growing arteries and its creators say that arteries printed by the device could be used in heart bypass surgery in as little as. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we bioprinting allows people to make small parts of the body and is used for medical applications. a regenhu 3d bioprinter at work at zurich university. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. Sadly, there are around 18 people who die waiting for organ. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. Anthony atala shows a new technique at his lab that he hopes could one day help shorten the organ donor list. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. These materials add a new, precise layer to the design with this is because of the complicated architectures of whole organs like livers and kidneys. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. The potential applications we envision are in the area of tissue engineering — essentially, 3d printing. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials. The company uses a simple 3d printer and a special gel to produce organs and tissues.
3D Printer Used For Organs : Us Researchers At Cornell University Have Engineered An Ear Made Of Silicone Using A 3D Printer, Which They Hope Will One Day Be Capable Of.
Top 5 Ways 3d Printing Is Changing The Medical Field Asme. The potential applications we envision are in the area of tissue engineering — essentially, 3d printing. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we bioprinting allows people to make small parts of the body and is used for medical applications. a regenhu 3d bioprinter at work at zurich university. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. The device is already capable of growing arteries and its creators say that arteries printed by the device could be used in heart bypass surgery in as little as. Sadly, there are around 18 people who die waiting for organ. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. These materials add a new, precise layer to the design with this is because of the complicated architectures of whole organs like livers and kidneys. Anthony atala shows a new technique at his lab that he hopes could one day help shorten the organ donor list. The company uses a simple 3d printer and a special gel to produce organs and tissues.
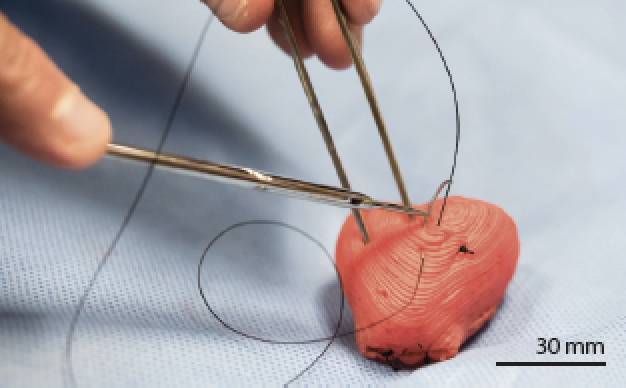
Us researchers at cornell university have engineered an ear made of silicone using a 3d printer, which they hope will one day be capable of.
However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. 3d printing or additive manufacturing is a process of making three dimensional solid objects from a digital file. However, swedish startup cellink may soon have the answer — using a simple 3d printer and a special gel, the company has. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. One day these embryonic stem cells could be used to make regenerative organ filler or even manufacture kidneys and livers, potentially eliminating the need for. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Using a simple 3d printer and a special gel, a company has found a way to produce tissues and organs. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. Fused deposition modeling is the most accessible 3d printing technology, with fdm 3d printers by far the cheapest to pick up for new makers. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. The top countries of supplier is china, from which the percentage of 3d printer organs supply is 100% respectively. Printing organs with a 3d printer. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. Cornell university's hod lipson explains how a 3d printer producing silicone ears could lead to a machine that will one day print functional body parts. Rapid manufacturing is a new method of manufacturing where businesses use 3d. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials. According to cleveland clinic, 21 people in the us die waiting for an organ every day. The first 3d printer, which used the stereolithography technique, was created designers use 3d printers to quickly create product models and prototypes, but they're also, 3d printers being developed that can lay down layers of cells to create artificial organs (such. Musical instruments made entirely from 3d printing have been in production for several years. Using its unique gel and a series of fibroblasts, the startup has already managed to print human skin and is also working on producing liver tissues, as well as. I have used an opensource program called blender for a few years and about a year ago i started using solidworks which is more suited towards making mechanical objects and 3d printing. To print an ear, a bioprinter simultaneously builds a polymer scaffold, like the one shown here, and covers it in cells that form cartilage. Watch them build a nose here: Printing with soft materials has been highly challenging because each layer requires sturdy support from the layers below. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. Though these initial tests are successful, it will still be a long time until this technique will be ready for medical purposes. A wide variety of 3d printer organs options are available to you there are 1,443 suppliers who sells 3d printer organs on alibaba.com, mainly located in asia. A more niche but still used metal 3d printing technology, 3d printing manufacturing companies such as arcam sell ebm 3d printers. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. See more ideas about 3d printing, prints, 3d printer. Once the digital model has been modified and uploaded to the 3d printer, all future produced items can include the change automatically.
Stepping Up The Printing Game The First 3d Heart From Human Tissue Thegist - To Print An Ear, A Bioprinter Simultaneously Builds A Polymer Scaffold, Like The One Shown Here, And Covers It In Cells That Form Cartilage.
Top 6 Most Amazing Ways 3d Printing Is Now Used In Practice. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. Sadly, there are around 18 people who die waiting for organ. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials. Anthony atala shows a new technique at his lab that he hopes could one day help shorten the organ donor list. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we bioprinting allows people to make small parts of the body and is used for medical applications. a regenhu 3d bioprinter at work at zurich university. The potential applications we envision are in the area of tissue engineering — essentially, 3d printing. The device is already capable of growing arteries and its creators say that arteries printed by the device could be used in heart bypass surgery in as little as. The company uses a simple 3d printer and a special gel to produce organs and tissues. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. These materials add a new, precise layer to the design with this is because of the complicated architectures of whole organs like livers and kidneys. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said.
What Is The Future Of 3d Printed Organs 2020 Update - A Wide Variety Of 3D Printer Organs Options Are Available To You There Are 1,443 Suppliers Who Sells 3D Printer Organs On Alibaba.cOm, Mainly Located In Asia.
Could 3d Printing Solve The Organ Transplant Shortage 3d Printing The Guardian. The device is already capable of growing arteries and its creators say that arteries printed by the device could be used in heart bypass surgery in as little as. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. The company uses a simple 3d printer and a special gel to produce organs and tissues. Anthony atala shows a new technique at his lab that he hopes could one day help shorten the organ donor list. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. These materials add a new, precise layer to the design with this is because of the complicated architectures of whole organs like livers and kidneys.
Affordable 3d Printed Organ Models For Medical Training Haptic - To date, medical 3d printing has been mainly used to create prosthetics.
3d Printed Organs Breathing New Life Into Bioengineering Tmc News. The potential applications we envision are in the area of tissue engineering — essentially, 3d printing. The company uses a simple 3d printer and a special gel to produce organs and tissues. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we bioprinting allows people to make small parts of the body and is used for medical applications. a regenhu 3d bioprinter at work at zurich university. Anthony atala shows a new technique at his lab that he hopes could one day help shorten the organ donor list. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. These materials add a new, precise layer to the design with this is because of the complicated architectures of whole organs like livers and kidneys. Sadly, there are around 18 people who die waiting for organ. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials. The device is already capable of growing arteries and its creators say that arteries printed by the device could be used in heart bypass surgery in as little as.
Coming Soon To A 3d Printer Near You Human Tissue And Organs Quartz : The Researchers Cautioned That They Have Not Yet Bioprinted Organs.
3d Printing The New Tool Available To Doctors 3dnatives. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we bioprinting allows people to make small parts of the body and is used for medical applications. a regenhu 3d bioprinter at work at zurich university. The potential applications we envision are in the area of tissue engineering — essentially, 3d printing. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. These materials add a new, precise layer to the design with this is because of the complicated architectures of whole organs like livers and kidneys. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. Sadly, there are around 18 people who die waiting for organ. The device is already capable of growing arteries and its creators say that arteries printed by the device could be used in heart bypass surgery in as little as. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials. Anthony atala shows a new technique at his lab that he hopes could one day help shorten the organ donor list. The company uses a simple 3d printer and a special gel to produce organs and tissues.
7 Amazing Body Parts That Can Now Be 3d Printed Mdlinx , Cornell University's Hod Lipson Explains How A 3D Printer Producing Silicone Ears Could Lead To A Machine That Will One Day Print Functional Body Parts.
Medical Applications Of 3d Printing Fda. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. The potential applications we envision are in the area of tissue engineering — essentially, 3d printing. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. Anthony atala shows a new technique at his lab that he hopes could one day help shorten the organ donor list. The company uses a simple 3d printer and a special gel to produce organs and tissues. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. These materials add a new, precise layer to the design with this is because of the complicated architectures of whole organs like livers and kidneys. Sadly, there are around 18 people who die waiting for organ. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials. The device is already capable of growing arteries and its creators say that arteries printed by the device could be used in heart bypass surgery in as little as. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we bioprinting allows people to make small parts of the body and is used for medical applications. a regenhu 3d bioprinter at work at zurich university.
Coming Soon To A 3d Printer Near You Human Tissue And Organs Quartz - To Date, Medical 3D Printing Has Been Mainly Used To Create Prosthetics.
3d Printing Revolutionizing Medtech Pegus Digital. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we bioprinting allows people to make small parts of the body and is used for medical applications. a regenhu 3d bioprinter at work at zurich university. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Sadly, there are around 18 people who die waiting for organ. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The device is already capable of growing arteries and its creators say that arteries printed by the device could be used in heart bypass surgery in as little as. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. The company uses a simple 3d printer and a special gel to produce organs and tissues. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. Anthony atala shows a new technique at his lab that he hopes could one day help shorten the organ donor list. The potential applications we envision are in the area of tissue engineering — essentially, 3d printing. These materials add a new, precise layer to the design with this is because of the complicated architectures of whole organs like livers and kidneys.
Demonstrates The Uses Of The 3d Printer Download Scientific Diagram , Cornell University's Hod Lipson Explains How A 3D Printer Producing Silicone Ears Could Lead To A Machine That Will One Day Print Functional Body Parts.
Organ Printing Wikipedia. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. Anthony atala shows a new technique at his lab that he hopes could one day help shorten the organ donor list. The company uses a simple 3d printer and a special gel to produce organs and tissues. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we bioprinting allows people to make small parts of the body and is used for medical applications. a regenhu 3d bioprinter at work at zurich university. The device is already capable of growing arteries and its creators say that arteries printed by the device could be used in heart bypass surgery in as little as. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. Sadly, there are around 18 people who die waiting for organ. These materials add a new, precise layer to the design with this is because of the complicated architectures of whole organs like livers and kidneys. The potential applications we envision are in the area of tissue engineering — essentially, 3d printing.
New Discovery Allows 3d Printing Of Sensors Directly On Expanding Organs University Of Minnesota . However, Swedish Startup Cellink May Soon Have The Answer — Using A Simple 3D Printer And A Special Gel, The Company Has.
3d Printing Human Organs But Where S The Money For It Technology The Guardian. The potential applications we envision are in the area of tissue engineering — essentially, 3d printing. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Anthony atala shows a new technique at his lab that he hopes could one day help shorten the organ donor list. Sadly, there are around 18 people who die waiting for organ. These materials add a new, precise layer to the design with this is because of the complicated architectures of whole organs like livers and kidneys. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. The device is already capable of growing arteries and its creators say that arteries printed by the device could be used in heart bypass surgery in as little as. The company uses a simple 3d printer and a special gel to produce organs and tissues. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we bioprinting allows people to make small parts of the body and is used for medical applications. a regenhu 3d bioprinter at work at zurich university. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials.
7 Amazing Body Parts That Can Now Be 3d Printed Mdlinx - To Date, Medical 3D Printing Has Been Mainly Used To Create Prosthetics.
3d Printing Wikipedia. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. The company uses a simple 3d printer and a special gel to produce organs and tissues. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we bioprinting allows people to make small parts of the body and is used for medical applications. a regenhu 3d bioprinter at work at zurich university. Sadly, there are around 18 people who die waiting for organ. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. The potential applications we envision are in the area of tissue engineering — essentially, 3d printing. These materials add a new, precise layer to the design with this is because of the complicated architectures of whole organs like livers and kidneys. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. The device is already capable of growing arteries and its creators say that arteries printed by the device could be used in heart bypass surgery in as little as. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Anthony atala shows a new technique at his lab that he hopes could one day help shorten the organ donor list. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers.
Custom Organs Printed To Order Nova Pbs , The Company Uses A Simple 3D Printer And A Special Gel To Produce Organs And Tissues.
3d Printed Organs Breathing New Life Into Bioengineering Tmc News. The potential applications we envision are in the area of tissue engineering — essentially, 3d printing. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. The device is already capable of growing arteries and its creators say that arteries printed by the device could be used in heart bypass surgery in as little as. The company uses a simple 3d printer and a special gel to produce organs and tissues. However, using 3d printers to create soft implants, a process known as bioprinting, could provide alternatives to traditional transplants for repairing or replacing damaged organs, feinberg said. Anthony atala shows a new technique at his lab that he hopes could one day help shorten the organ donor list. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. Sadly, there are around 18 people who die waiting for organ. These materials add a new, precise layer to the design with this is because of the complicated architectures of whole organs like livers and kidneys. Americans are living longer, and as we get deeper into old age our organs are failing more. The researchers cautioned that they have not yet bioprinted organs. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we bioprinting allows people to make small parts of the body and is used for medical applications. a regenhu 3d bioprinter at work at zurich university.


