3D Printing Human Organs. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we in the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. Imagine printing a human liver. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. What led to first organic molecules. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. This process involves gradual addition of materials from the. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Singapore university of technology and design.
3D Printing Human Organs . A New Review Looks At The Likelihood Of 3D Printed Organs And Analyzes Recent Accomplishments, Limitations And Opportunities For Future Research.
3d Printed Hearts With Beating Tissue Could Ease Organ Donor Shortage. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Imagine printing a human liver. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Singapore university of technology and design. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. What led to first organic molecules. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. This process involves gradual addition of materials from the. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we in the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body.
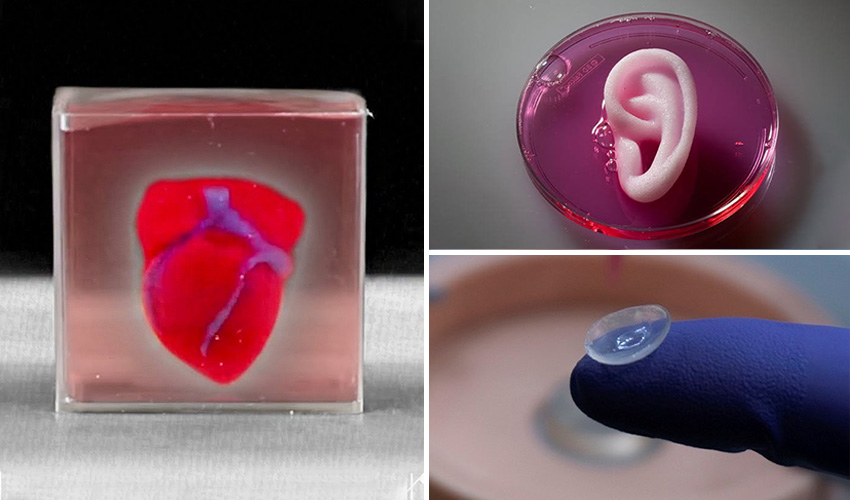
► subscribe for more tech & culture.
For example, printed organs that may not be suitable for humans could still benefit drug or vaccine testing. At first, the idea of 3d printing organs for transplant 'on demand' sounds like something out of the movies. Similar to normal 3d printers it deposits cells and structural and nutritional material in the attempt to combine different tissues to form organs. Swedish firm cellink is at that forefront of producing human ears and noses through 3d printing. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing. Scientists are hoping that human organs 3d printed in microgravity will function better thanks to a more precise structure. They have discovered a way to print incredibly lifelike models of human organs and various other parts of the anatomy. In 5th european conference of the international federation for medical and biological laser printing of skin cells and human stem cells. What led to first organic molecules. You turn a corner in a laboratory, and there's a table full of human aortas. And then we can actually replicate exactly the same. However, machines that promise to regenerate living human tissue, replace vital organs and quickly heal open wounds are a lot closer to reality than you may realize. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. Singapore university of technology and design. We will be using similar strategies to print solid organs. 3d printing is a type of additive manufacturing technique wherein, unlike subtractive manufacturing, the material is added layer by layer. Have you heard of other innovative medical uses for 3d printing? 216shares1703973d printing organs and body parts to serve as surgical aids is a trend that has been gathering steam within the industry for some time now. Researchers are dashing to make supplanting human organs with bio 3d printers. Bioprinting organs for human uses won't happen anytime soon, said tony atala, director of the wake forest institute for regenerative medicine in 7 cool uses of 3d printing in medicine. 3d bioprinting, the process of using bioink composed of tissue or human cells, has come a long way over the last decade. 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. It currently makes them for testing, but in future, aims to make human organs for transplantation. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that. In a 3d printing first, scientists have figured out how to print artificial versions of the body's complex vascular networks, which the heart and brain are often thought to be the most complex human organs, but other, equally nuanced body parts have proven to be just as difficult to recreate in the lab. For example, printed organs that may not be suitable for humans could still benefit drug or vaccine testing.
Human Organs On Demand Research 5 The 3dexperience Magazine 3ds Compass Mag . Singapore University Of Technology And Design.
How Close Are 3d Printed Organs To Reality Verdict. What led to first organic molecules. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. This process involves gradual addition of materials from the. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Imagine printing a human liver. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we in the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. Singapore university of technology and design. ► subscribe for more tech & culture.
Custom Organs Printed To Order Nova Pbs - Bioengineers At Rice University Created Entangled Cardiovascular Networks Similar To The Body's Natural Passageways.
Researchers Just 3d Printed The First Ever Complete Heart Using Human Tissue. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. This process involves gradual addition of materials from the. Imagine printing a human liver.
How 3d Printing Is Changing Health And Medicine , Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways.
Human Organ Transplants Could Be 3d Printed In 15 Years Russian Researchers Rt World News. This process involves gradual addition of materials from the. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Imagine printing a human liver. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. What led to first organic molecules. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Singapore university of technology and design. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we in the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs.
How Medical 3d Printing Could Solve The Shortage Of Organ Donations Youtube : They'rE Also Less Likely To Be Rejected By The Body.
A Swifter Way Towards 3d Printed Organs Technology Networks. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. What led to first organic molecules. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Imagine printing a human liver. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Singapore university of technology and design. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. This process involves gradual addition of materials from the. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we in the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs.
Here S How 3d Printers Are Making Human Body Parts Cellink China : 3D Bioprinting, The Process Of Using Bioink Composed Of Tissue Or Human Cells, Has Come A Long Way Over The Last Decade.
3d Printing Organs Moves A Few More Steps Closer To Commercialization Techcrunch. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we in the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. Singapore university of technology and design. What led to first organic molecules. This process involves gradual addition of materials from the. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Imagine printing a human liver. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. ► subscribe for more tech & culture.
Can 3d Printing Help The Organ Shortage Lifecenter . Similar To Normal 3D Printers It Deposits Cells And Structural And Nutritional Material In The Attempt To Combine Different Tissues To Form Organs.
3d Printing Of Human Organs. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we in the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. Singapore university of technology and design. What led to first organic molecules. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Imagine printing a human liver. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. This process involves gradual addition of materials from the. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways.
Is 3d Bioprinting The Future Of Tailor Made Medicine 3dnatives - Microgravity Can Help Us Obtain Biosamples With A Larger Percentage Of Viable Cells, Said Dmitry Serin, Deputy Head Of The.
3d Printing In Plain English Throomers Cool Stuff. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. This process involves gradual addition of materials from the. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. What led to first organic molecules. Singapore university of technology and design. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we in the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Imagine printing a human liver. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs.
3d Printed Kidneys Take Small Steps Toward Organ Replacements Live Science - What Led To First Organic Molecules.
3d Printed Organs Nearing Clinical Trials Asme. Imagine printing a human liver. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. What led to first organic molecules. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Singapore university of technology and design. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we in the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. This process involves gradual addition of materials from the. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing.
Silicon Valley Startup 3d Printing Human Organs To Save Lives - The Problem Is That Even The Simplest Human Organs Are Structurally Complex.
Scientists Can Now 3d Print Functional Organs Youtube. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we in the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. This process involves gradual addition of materials from the. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. What led to first organic molecules. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Singapore university of technology and design. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Imagine printing a human liver.
Could 3d Printing Solve The Organ Transplant Shortage 3d Printing The Guardian , What Led To First Organic Molecules.
Scientists Successfully 3d Print Human Muscle Tissue Digital Trends. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Traditional 3d printer technology relies on the process of additive manufacturing. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. What led to first organic molecules. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we in the beginning, this might mean printing skin or cartilage, which are relatively simple structures and are more straightforward to grow outside the body. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. With new developments in the field of biofabrication, it is now possible to print out human organs. Imagine printing a human liver. Singapore university of technology and design. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. This process involves gradual addition of materials from the. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers.


