3D Printing Of Organs And Tissues. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues.
3D Printing Of Organs And Tissues : 3D Printed Organs Are A Quest For Myriad Of Companies.
A Swifter Way Towards 3d Printed Organs Tectales Tagging Medical Technology. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said.
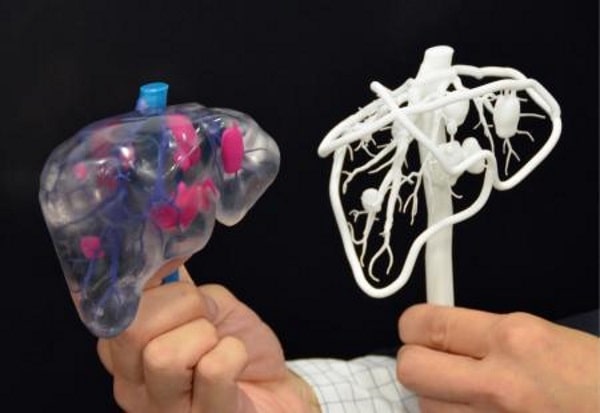
In reality, printed organs are a long way away.
The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; Like the electrospun matrix, the. I am amazed about the technology advancement in organs and tissues. This technology is advancing so rapidly that 3d printed organs for use in human transplantations could be a reality sooner than we think. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Once the integrated tissue and organ printing system (itop) is further tested, and has been proven to be safe for use in humans, we could soon be printing out replacement when printing human tissues and organs, of course, we need to make sure the cells survive, and function is the final test. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. In february, cornell university in ithaca, new york, announced it had used 3d. Every day an average of 18 people die waiting for an organ transplant in the united states. When printing human tissues and organs, of course, we need to make sure the cells survive, and function is the final test. Tissues of various organs are formed using 3d bioprinting involving blood vessels, bone, cartilage, heart, kidneys, and that of the skin and neurons. Eventually, a range of tissues can be printed together to form an organ. It is an ink formulation that dictates the printing of living cells. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. To create a solid organ, researchers need a way to promote the growth of blood vessels so that every cell in the organ receives the this skeleton is made of collagen, a protein found in the body's connective tissue and its extracellular matrices. It prints 3d structures, in this case, biological tissues, by successively layering microdrops of cells on a surface. how far away are we from bioprinting our organs? Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated in the near term, tissues and organs grown on such scaffolds might also find use as sophisticated, 3d tissue chips, with potential for use in studies. Over the last two decades, a wide variety of 3d printing technologies have been adapted to hard tissue and organ engineering. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Estimates for a date when organ bioprinting will be viable vary wildly, with one team claiming that they will be able to bioprint a heart. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. How to print solid organs? While it's become increasingly apparent that 3d printing hasn't proven overly useful for the average consumer, it's showing real promise in other areas. These new forms of printing, should they be realised, will, it is argued, have the same revolutionary and democratising effect as book printing in their applicability to regenerative medicine building on these two processes, organoids, the functional building blocks of tissues and organs, are constructed.
3d Printed Organs And Tissues Internetmedicine Com . In Reality, Printed Organs Are A Long Way Away.
Prellis Biologics Achieves Unprecedented Speed And Resolution In 3d Printing Of Human Tissue With Capillaries Synbiobeta. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts.
3d Printing For Implantable Medical Devices From Surgical Reconstruction To Tissue Organ Regeneration Frontiers Research Topic : Donated Organs Are Tough To Come By, Which Is Why Many Scientists Have Spent The Last Two Decades Trying To Create New Livers, Kidneys, Hearts Or Lungs From Scratch.
India 3d Bio Printing Of Tissues Organs 3d Printing Today 3d Printing News And 3d Printing Trends. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced.
On The Road To 3 D Printed Organs The Scientist Magazine : Hard tissues and organs, including the bones, teeth and cartilage, are the most extensively exploited and rapidly developed areas in regenerative medicine field.
Prellis Biologics Achieves Unprecedented Speed And Resolution In 3d Printing Of Human Tissue With Capillaries Synbiobeta. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs.
Mike Renard 3d Printing Organs And Tissues Interview . While It's Become Increasingly Apparent That 3D Printing Hasn't Proven Overly Useful For The Average Consumer, It's Showing Real Promise In Other Areas.
3d Bioprinting Using Stem Cells Pediatric Research. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies.
India 3d Bio Printing Of Tissues Organs 3d Printing Today 3d Printing News And 3d Printing Trends . But Prof Atala Said 3D Printing.
3d Printing For Human Organs And Tissue Nih Medlineplus Magazine. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said.
A Bff In Space Bioprinter Will 3d Print Human Tissue On The Space Station Space . It's Not The Mechanical Process That's The Problem Here;
3d Bioprinting Creates Collagen To Rebuild Hearts Physics World. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least.
Challenges Of 3d Bioprinting Biogelx - In February, Cornell University In Ithaca, New York, Announced It Had Used 3D.
This 3d Printer Creates Human Muscles And Tissues That Could Actually Replace Real Ones Quartz. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is.
Implantable 3d Printed Organs Could Be Coming Sooner Than You Think Techcrunch - In Reality, Printed Organs Are A Long Way Away.
India 3d Bio Printing Of Tissues Organs 3d Printing Today 3d Printing News And 3d Printing Trends. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies.
A 3d Bioprinting System To Produce Human Scale Tissue Constructs With Structural Integrity Nature Biotechnology - In The Next 10 Years It Is Possible That Printed Supplemental Tissues, Ones That Aid In Alongside Human Tissue, 3D Printing Is Being Used To Develop Body Parts.
How 3d Printing Is Changing Health And Medicine. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time.
Israeli Scientists Create World S First 3d Printed Heart Using Human Cells - The Quest To 'pRint Living Replacement Organs' Is Founded On Insatiable Organovo Is Perhaps The Most Prominent Company Conducting Research Into The 3D Bioprinting Process For Live Tissues And 3D Printed Organs, At Least.
How A Centuries Old Sculpting Method Is Helping 3d Print Organs With Blood Vessels. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed supplemental tissues, ones that aid in alongside human tissue, 3d printing is being used to develop body parts. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. The path to printing an organ is far from easy though and many problems have to be solved with regards to bioprinters more than 450 scientists collaborate on regenerative medicine research at the institute, the largest in the world, working on more than 40 different tissues and organs. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. In reality, printed organs are a long way away.


