3D Printing Organs Article. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Beyond direct organ transplants, 3d printing can be used to benefit many different aspects of the medical world. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Helping to not only produce donor organs but to also provide better healing for patients and education for medical staff and students. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. To conclude this article, however, here's a warning that came from the most unlikely of sources — red dwarf. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. We can't overstate how much we appreciate people that have the talent to use humor to make a serious point. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers.
3D Printing Organs Article , Instead Of Printing Layer Upon Layer Of Living Cells To Form A 3D Structure, Like.
3d Bioprinting Bioink Selection Guide Sigma Aldrich. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Helping to not only produce donor organs but to also provide better healing for patients and education for medical staff and students. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Beyond direct organ transplants, 3d printing can be used to benefit many different aspects of the medical world. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. We can't overstate how much we appreciate people that have the talent to use humor to make a serious point. To conclude this article, however, here's a warning that came from the most unlikely of sources — red dwarf. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material;
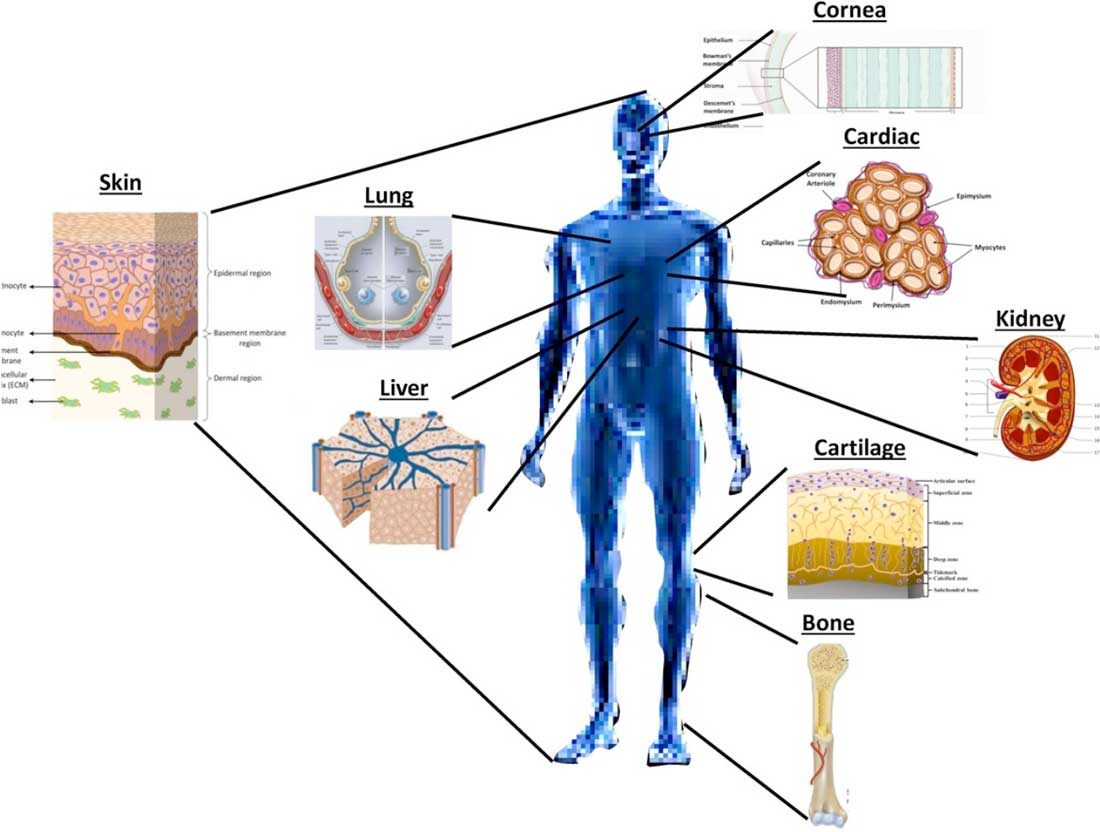
But no one has been able to 'print' the complicated systems of fine blood vessels that run through organs, rendering fabricated lung or heart muscle useless.
Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. But no one has been able to 'print' the complicated systems of fine blood vessels that run through organs, rendering fabricated lung or heart muscle useless. Bioprinting is quickly gaining traction. One day we might be able to print replacement organs for those who need them. However, you cannot print an organ with any vascular networks. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. What they have learnt so far is that the fabrication of inanimate objects is easier than living body parts. Will we one day soon be 3d printing organs which are unlike anything seen before in humans? How to print solid organs? Let's say a patient presented with an injury to. From prosthetic limbs and various surgical devices made with plastics and metals, to using cells to print human organs, experiments in this industry are progressing quickly. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; Printed & flexible electronics overview report flexible, printed and organic electronics 3d electronics barrier films and thin film encapsulation for one of the limits in achieving 3d bioprinted organs for transplant is size. Scientists have developed a way to 3d. A novel tissue engineering paradigm. 3d bioprinting of tissues and organs. To create a solid organ, researchers need a way to promote the growth of blood vessels so that every cell in the organ receives the oxygen and nutrients and it can eliminate waste. What's next for 3d printing? The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. In a 3d printing first, scientists have figured out how to print artificial versions of the body's complex vascular networks, which mimic our natural passageways for blood, air, lymph creating functional tissue replacements is a high scientific priority because of its potential impact on organ donations. Evolution is what got us here today, if you accept the scientific approach to our creation. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Printing tiny organs for 'body on a chip']. In 5th european conference of the international federation for medical and biological towards organ printing: He told the bbc news website: 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. Swedish firm cellink is at that forefront of producing human ears and noses through 3d printing. Beyond direct organ transplants, 3d printing can be used to benefit many different aspects of the medical world. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material;
3d Printing Of Human Organs Future Perspective Ip Scenario Aranca . Perfectly Fabricating Organs Mean Fewer Chances Of Failure Or Rejection.
Pdf 3d Bioprinting Of Tissues And Organs. Beyond direct organ transplants, 3d printing can be used to benefit many different aspects of the medical world. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Helping to not only produce donor organs but to also provide better healing for patients and education for medical staff and students. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. To conclude this article, however, here's a warning that came from the most unlikely of sources — red dwarf. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. We can't overstate how much we appreciate people that have the talent to use humor to make a serious point. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has.
Your Health Checkup 3d Printing Joints Tissue And Even Organs The Saturday Evening Post : However, You Cannot Print An Organ With Any Vascular Networks.
Sutd Researchers Create Heart Cells From Stem Cells Using 3d Printing Eurekalert Science News. Helping to not only produce donor organs but to also provide better healing for patients and education for medical staff and students. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has. To conclude this article, however, here's a warning that came from the most unlikely of sources — red dwarf. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like.
Visual Wednesdays The State Of 3d Printing In Medicine Rock Health . How to print solid organs?
3d Organ Printing A Way To Liver A Little Longer Rice Catalyst. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. We can't overstate how much we appreciate people that have the talent to use humor to make a serious point. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has. Helping to not only produce donor organs but to also provide better healing for patients and education for medical staff and students. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. To conclude this article, however, here's a warning that came from the most unlikely of sources — red dwarf. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Beyond direct organ transplants, 3d printing can be used to benefit many different aspects of the medical world. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers.
3d Printed Hearts With Beating Tissue Could Ease Organ Donor Shortage . To Create A Solid Organ, Researchers Need A Way To Promote The Growth Of Blood Vessels So That Every Cell In The Organ Receives The Oxygen And Nutrients And It Can Eliminate Waste.
The Importance Of 3d Printing Mesenchymal Stem Cells In. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has. Beyond direct organ transplants, 3d printing can be used to benefit many different aspects of the medical world. To conclude this article, however, here's a warning that came from the most unlikely of sources — red dwarf. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. We can't overstate how much we appreciate people that have the talent to use humor to make a serious point. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Helping to not only produce donor organs but to also provide better healing for patients and education for medical staff and students. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers.
Print Me An Organ Why Are We Not There Yet , »»» Subscribe To The National To Watch More Videos Here.
How 3d Bioprinting Could Revolutionize Organ Replacement Bostonomix. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has. To conclude this article, however, here's a warning that came from the most unlikely of sources — red dwarf. Helping to not only produce donor organs but to also provide better healing for patients and education for medical staff and students. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Beyond direct organ transplants, 3d printing can be used to benefit many different aspects of the medical world. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. We can't overstate how much we appreciate people that have the talent to use humor to make a serious point. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. 3d printing organs is now on the list too.
3d Printing The Stem Cellar : Let's Say A Patient Presented With An Injury To.
The Next Frontier In 3 D Printing Human Organs Cnn. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. We can't overstate how much we appreciate people that have the talent to use humor to make a serious point. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. To conclude this article, however, here's a warning that came from the most unlikely of sources — red dwarf. Helping to not only produce donor organs but to also provide better healing for patients and education for medical staff and students. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. Beyond direct organ transplants, 3d printing can be used to benefit many different aspects of the medical world. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers.
Can 3 D Printing Produce Lung And Liver Tissue For Transplants Scientific American - He Told The Bbc News Website:
3d Printing The Stem Cellar. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Beyond direct organ transplants, 3d printing can be used to benefit many different aspects of the medical world. We can't overstate how much we appreciate people that have the talent to use humor to make a serious point. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Helping to not only produce donor organs but to also provide better healing for patients and education for medical staff and students. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. To conclude this article, however, here's a warning that came from the most unlikely of sources — red dwarf. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer.
3d Printing Of Human Organs Future Perspective Ip Scenario Aranca - He Told The Bbc News Website:
Organ Bioprinting Gets A Breath Of Fresh Air. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. Beyond direct organ transplants, 3d printing can be used to benefit many different aspects of the medical world. Helping to not only produce donor organs but to also provide better healing for patients and education for medical staff and students. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; We can't overstate how much we appreciate people that have the talent to use humor to make a serious point. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. To conclude this article, however, here's a warning that came from the most unlikely of sources — red dwarf. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced.
3d Printed Hearts With Beating Tissue Could Ease Organ Donor Shortage : Evolution Is What Got Us Here Today, If You Accept The Scientific Approach To Our Creation.
Computer Aided Multiple Head 3d Printing System For Printing Of Heterogeneous Organ Tissue Constructs Scientific Reports. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has. Helping to not only produce donor organs but to also provide better healing for patients and education for medical staff and students. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. To conclude this article, however, here's a warning that came from the most unlikely of sources — red dwarf. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. We can't overstate how much we appreciate people that have the talent to use humor to make a serious point. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. Beyond direct organ transplants, 3d printing can be used to benefit many different aspects of the medical world. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material;
3d Printing In The Medical Field Four Major Applications Revolutionising The Industry Verdict Medical Devices : Will We One Day Soon Be 3D Printing Organs Which Are Unlike Anything Seen Before In Humans?
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcttw1mktbru3so8vmxafnzsdcs248vuzw7wja Usqp Cau. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. We can't overstate how much we appreciate people that have the talent to use humor to make a serious point. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Helping to not only produce donor organs but to also provide better healing for patients and education for medical staff and students. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like as we have mentioned in previous articles on additive manufacturing, 3d printing will go on to 3d printed organs could save people's lives. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has. Beyond direct organ transplants, 3d printing can be used to benefit many different aspects of the medical world. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. To conclude this article, however, here's a warning that came from the most unlikely of sources — red dwarf. 3d printing organs is now on the list too.


