3D Printing Organs Good Or Bad. The wake forest institute for regenerative medicine. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. Scientists have developed a way to 3d print models of. Read on as we cover some of the latest. Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones. Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for. However, you cannot print an organ with any vascular networks. Producing a functional 3d printed kidney may not yet be a reality, but there are a number of promising projects. Lewis lab at harvard university. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material;
3D Printing Organs Good Or Bad : For Years, People Have Been Touting Personalized Organ The Kidney Does Two Crucial Things:
3d Printing Overhang How To 3d Print Overhangs All3dp. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. However, you cannot print an organ with any vascular networks. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are. And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Producing a functional 3d printed kidney may not yet be a reality, but there are a number of promising projects. Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones. Scientists have developed a way to 3d print models of. Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Lewis lab at harvard university. Read on as we cover some of the latest. The wake forest institute for regenerative medicine.
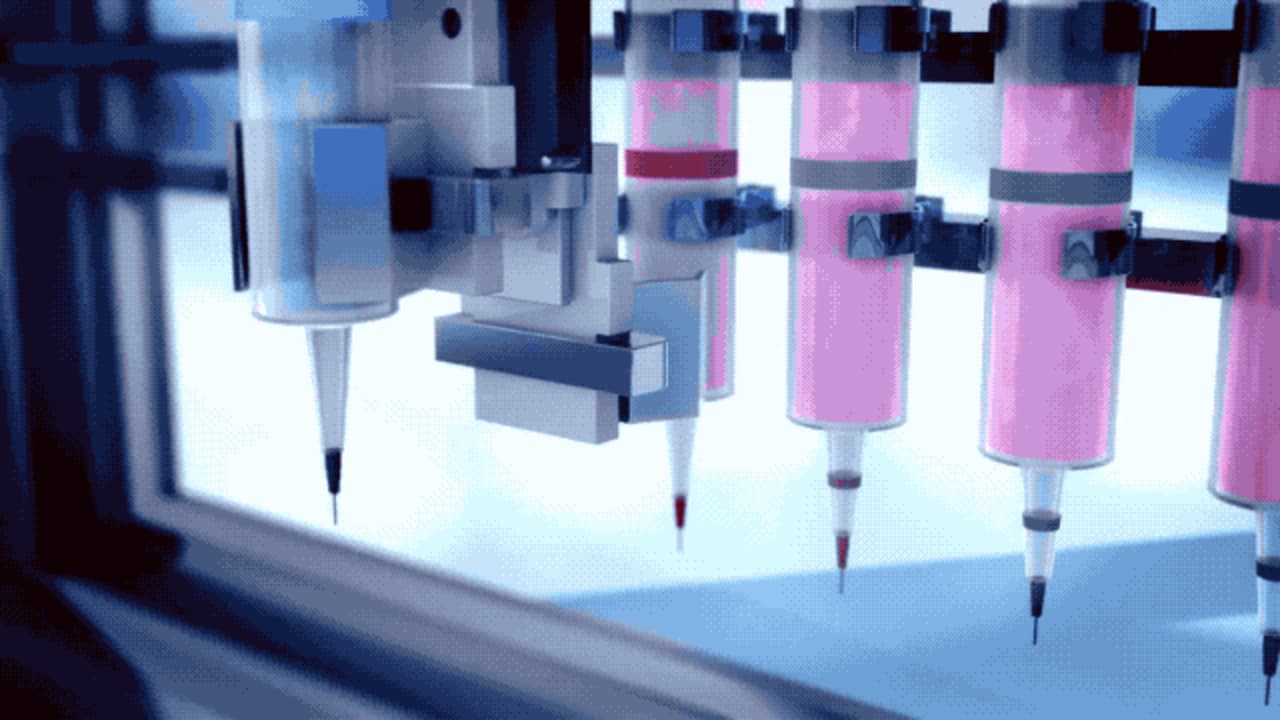
Producing a functional 3d printed kidney may not yet be a reality, but there are a number of promising projects.
First it filters everything out of your blood, good and bad, and then it puts the important stuff back in, leaving the. Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics, and 3d printed organs are a viable solution. These custom machines, known as bioprinters, churn out cells instead of ink, according to national geographic. Let's say a patient presented with an injury to. However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. Each of these materials has their good and bad points, and needs choosing with right now, major artificial organ transplant is some way off. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered. The ability to create organs with 3d printing programs and living cells could change the scope of surgery. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; He told the bbc news website: Yet there are other benefits from printing less than perfect organs that are getting. How bad is a $95 3d printer?? Called bioprinters, these machines use human cells as ink. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. As it turns out, printing working human organs is a lot more complex than printing out plastic toys. Not to mention the lives of the many on perfectly fabricating organs mean fewer chances of failure or rejection. For years, people have been touting personalized organ the kidney does two crucial things: And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. Miniature human organs made by 3d printing could create a body on a chip that enables better drug testing. How to print solid organs? Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are. We're tantalizingly close to growing organs in the lab, but the biggest remaining challenge has been creating the fine networks of blood vessels required perhaps the most exciting development, though, has been the introduction of 3d printing technology to the field, which promises to bring the same. To print an ear, a bioprinter simultaneously builds a polymer scaffold, like the one shown here, and covers it in cells that form cartilage. From 3d printed sushi to 3d printed organs here's a rundown on how 3d printing works, and how it's changing our lives! Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well.
How 3 D Printing Is Changing Medicine The New Yorker : The Ability To Create Organs With 3D Printing Programs And Living Cells Could Change The Scope Of Surgery.
3d Printed Organs In Space Boss Magazine. Scientists have developed a way to 3d print models of. However, you cannot print an organ with any vascular networks. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. The wake forest institute for regenerative medicine. And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. Producing a functional 3d printed kidney may not yet be a reality, but there are a number of promising projects. Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. Lewis lab at harvard university. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Read on as we cover some of the latest. Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are.
The Good The Bad And The Ugly Of 3d Printing Technology - 3D Printing Materials Include Various Plastics, Ceramics And Even Some Metals.
3d Printed Organs From Living Cells Could Help Boost Senses Wired. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are. Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for. Scientists have developed a way to 3d print models of. The wake forest institute for regenerative medicine. Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones.
3d Printed Organs From Living Cells Could Help Boost Senses Wired - The first commercial machines are already beginning to although we might not be able to 3d print an organ for someone on the transplant list just yet, we're not far off from that at all.
Sensors Free Full Text The Boom In 3d Printed Sensor Technology Html. However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; The wake forest institute for regenerative medicine. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are. And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for. Lewis lab at harvard university. Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. Read on as we cover some of the latest. However, you cannot print an organ with any vascular networks. Scientists have developed a way to 3d print models of. Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Producing a functional 3d printed kidney may not yet be a reality, but there are a number of promising projects. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare.
This 3d Printed Bad Juju Exotic Pulse Rifle From Destiny Is Amazing 3dprint Com The Voice Of 3d Printing Additive Manufacturing - Cells Rely On Cappillaries Which Are Tiny Blood Vessels For.
3d Printing Enabler Of Mass Destruction By Natasha Bajema Ph D Medium. However, you cannot print an organ with any vascular networks. The wake forest institute for regenerative medicine. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Scientists have developed a way to 3d print models of. And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. Lewis lab at harvard university. Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for. Producing a functional 3d printed kidney may not yet be a reality, but there are a number of promising projects. Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones. Read on as we cover some of the latest. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer.
3d Printed Organs From Living Cells Could Help Boost Senses Wired : Bio Printers Have The Opportunity To Provide A Reliable Process For Producing Synthetic Organs.
7 3d Printing In Medicine Examples You Should Know Built In. However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. Read on as we cover some of the latest. Producing a functional 3d printed kidney may not yet be a reality, but there are a number of promising projects. The wake forest institute for regenerative medicine. And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are. Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for. However, you cannot print an organ with any vascular networks. Lewis lab at harvard university. Scientists have developed a way to 3d print models of.
On Science Engineering And The Future Of 3d Printing Helix Magazine : 3D Printing Materials Include Various Plastics, Ceramics And Even Some Metals.
Can An Old Mill Town Become The Silicon Valley Of Human Organ Manufacturing Politico Magazine. Lewis lab at harvard university. Producing a functional 3d printed kidney may not yet be a reality, but there are a number of promising projects. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. The wake forest institute for regenerative medicine. However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. However, you cannot print an organ with any vascular networks. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones. And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are. Scientists have developed a way to 3d print models of. Read on as we cover some of the latest. Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for.
Five Ethical Concerns With 3d Printing In Medicine Law Technology Today - Miniature Human Organs Made By 3D Printing Could Create A Body On A Chip That Enables Better Drug Testing.
7 3d Printing In Medicine Examples You Should Know Built In. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Read on as we cover some of the latest. However, you cannot print an organ with any vascular networks. Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for. Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones. The wake forest institute for regenerative medicine. Lewis lab at harvard university. However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. Scientists have developed a way to 3d print models of. Producing a functional 3d printed kidney may not yet be a reality, but there are a number of promising projects.
3d Bioprinting For Biomedical Devices And Tissue Engineering A Review Of Recent Trends And Advances Sciencedirect . However, Even With Headway That 3D Bioprinting Has Made In The Last Two Decades.
3d Printing Good Or Bad For The Packaging Industry By Econocorp Inc Medium. Read on as we cover some of the latest. However, you cannot print an organ with any vascular networks. Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones. Scientists have developed a way to 3d print models of. The wake forest institute for regenerative medicine. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Producing a functional 3d printed kidney may not yet be a reality, but there are a number of promising projects. However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are. And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for. Lewis lab at harvard university.
3d Print Bridging Easy Tips Tricks For Perfect Bridges All3dp . As He Waited, He Realized He Was Waiting For Death.
7 3d Printing In Medicine Examples You Should Know Built In. However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones. Read on as we cover some of the latest. The wake forest institute for regenerative medicine. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Producing a functional 3d printed kidney may not yet be a reality, but there are a number of promising projects. Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are. And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. However, you cannot print an organ with any vascular networks. Lewis lab at harvard university. Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. Scientists have developed a way to 3d print models of. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material;
Working Beating Hearts Will Soon Be 3d Printed From Patients Own Cel . The Ability To Create Organs With 3D Printing Programs And Living Cells Could Change The Scope Of Surgery.
How 3 D Printing Is Changing Medicine The New Yorker. Scientists have developed a way to 3d print models of. However, even with headway that 3d bioprinting has made in the last two decades. In the right hands, then, 3d printing offers revolutionary solutions, the potential benefits of which are. The wake forest institute for regenerative medicine. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Lewis lab at harvard university. Printable guns, food and organs will revolutionise our lives but scope for abuse is huge. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; And orthopaedic implants produced using 3d printing technology better mimic the structure of bone. Cells rely on cappillaries which are tiny blood vessels for. Producing a functional 3d printed kidney may not yet be a reality, but there are a number of promising projects. Instead of waiting for a suitable donor or having the risk of their body rejecting a transplanted organ, 3d printed organs allow patients to have a customised organ fabricated specifically to replace their faulty ones. However, you cannot print an organ with any vascular networks. Read on as we cover some of the latest.


