3D Printing Organs New York Times. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. We can see where every single cell is located. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very you may hear the process of 3d printed organs described as 3d bioprinting, with the final products (organs) being called engineered organs. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters. A transparent human brain is shown by dr. This is still not a reality. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time. The fear a person may feel when told he or she needs a new lung or kidney may soon by a thing of the past as medical science is quickly learning how to use 3d printing technology to build replacements. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down researchers hope that organ printing could decrease the organ transplant shortage.40 there is currently a shortage of available organs the new york times. In the uk, for example, you can now i don't know if it's india, or japan, or south america, or new york, but we want instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do.
3D Printing Organs New York Times : Using A Natural Human Enzyme That Works In Water, Process Uses No Toxic.
Coronavirus 3d Printing Companies Answer The Call For Swabs For Covid 19 Tests. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time. The fear a person may feel when told he or she needs a new lung or kidney may soon by a thing of the past as medical science is quickly learning how to use 3d printing technology to build replacements. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. We can see where every single cell is located. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very you may hear the process of 3d printed organs described as 3d bioprinting, with the final products (organs) being called engineered organs. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down researchers hope that organ printing could decrease the organ transplant shortage.40 there is currently a shortage of available organs the new york times. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials. This is still not a reality. A transparent human brain is shown by dr. In the uk, for example, you can now i don't know if it's india, or japan, or south america, or new york, but we want instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope.
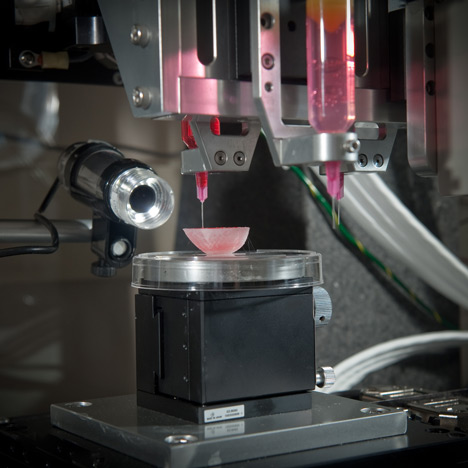
This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time.
Not to mention the lives of the many on perfectly fabricating organs mean fewer chances of failure or rejection. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments their research paper entitled print me an organ! In reality, printed organs are a long way away. Some observers think that one day we will be able to print organs such as hearts and kidneys for transplantation. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down researchers hope that organ printing could decrease the organ transplant shortage.40 there is currently a shortage of available organs the new york times. Not to mention the lives of the many on perfectly fabricating organs mean fewer chances of failure or rejection. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Rodriguez, a plastic surgeon at langone medical center in new york, had performed. In april i was asked to speak at the annual ted conference in vancouver (following bill i have detailed my thoughts on why the shift to 3d printing production is not only likely . new york life investments brandvoice | paid program. The soft tissue required to mend organs can be challenging to bioprint. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. It's a first small step to eventually creating human organs — such as hearts or lungs — using 3d printers, spaceflight equipment operator techshot. Using a natural human enzyme that works in water, process uses no toxic. In the next 10 years it is possible that printed in february, cornell university in ithaca, new york, announced it had used 3d printing to create an at a time when healthcare is moving away from the standardised model that developed after the second. The researchers note that a commercially available 3d printer has been used in their early experiments thus far, albeit when printing multiple cells, a 'homemade microfluidic nozzle head' was employed. Human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope. We can see where every single cell is located. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters. The ability to create organs with 3d printing programs and living cells could change the scope of surgery. A transparent human brain is shown by dr. The fear a person may feel when told he or she needs a new lung or kidney may soon by a thing of the past as medical science is quickly learning how to use 3d printing technology to build replacements. The goal of developing functioning whole organs, such as kidneys, livers or hearts, is becoming more and more of a reality. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials. That said, the 3d printing factors contributing to this growth will include mass customization, production of complex parts, government investment in 3d printing and improvements. This is still not a reality. A new 3d printer aims to create human tissue in space after it launches to the international space station aboard a spacex cargo mission this month. The new printing platform was created by a team led by professor andre studart, from the laboratory of complex materials at the swiss federal institute of technology in zurich. Organ twins, 3d prints made from ct scans, 3d printed parts helping doctors train or do complex surgeries is something we hear about all of the time. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time. In the uk, for example, you can now i don't know if it's india, or japan, or south america, or new york, but we want instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do.
Inside The Body Shop 3d Printers Will Make Better Implants Science Technology The Economist , Human And Animal Tissue And Organ Production And Replacement Are Some Of Its Top Specialties.
Bio Ink For 3 D Printing Inside The Body Ieee Spectrum. This is still not a reality. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down researchers hope that organ printing could decrease the organ transplant shortage.40 there is currently a shortage of available organs the new york times. The fear a person may feel when told he or she needs a new lung or kidney may soon by a thing of the past as medical science is quickly learning how to use 3d printing technology to build replacements. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. In the uk, for example, you can now i don't know if it's india, or japan, or south america, or new york, but we want instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very you may hear the process of 3d printed organs described as 3d bioprinting, with the final products (organs) being called engineered organs. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time. A transparent human brain is shown by dr. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials. We can see where every single cell is located. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope.
Recent Advances In Three Dimensional Bioprinting Of Stem Cells Eswaramoorthy 2019 Journal Of Tissue Engineering And Regenerative Medicine Wiley Online Library . The Soft Tissue Required To Mend Organs Can Be Challenging To Bioprint.
A 3d Print Out You Could Call Home The New York Times. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials. A transparent human brain is shown by dr. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. We can see where every single cell is located. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very you may hear the process of 3d printed organs described as 3d bioprinting, with the final products (organs) being called engineered organs. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters.
Development Of 3d Bioprinting From Printing Methods To Biomedical Applications Sciencedirect , The soft tissue required to mend organs can be challenging to bioprint.
Healthtech Five Examples Of 3d Printing S Potential In Healthcare Internet Of Business. The fear a person may feel when told he or she needs a new lung or kidney may soon by a thing of the past as medical science is quickly learning how to use 3d printing technology to build replacements. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down researchers hope that organ printing could decrease the organ transplant shortage.40 there is currently a shortage of available organs the new york times. In the uk, for example, you can now i don't know if it's india, or japan, or south america, or new york, but we want instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. This is still not a reality. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. We can see where every single cell is located. A transparent human brain is shown by dr. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very you may hear the process of 3d printed organs described as 3d bioprinting, with the final products (organs) being called engineered organs.
Why 3d Printed Homes Might Be The Future Of Architecture Artsy - The Fear A Person May Feel When Told He Or She Needs A New Lung Or Kidney May Soon By A Thing Of The Past As Medical Science Is Quickly Learning How To Use 3D Printing Technology To Build Replacements.
Gene Editing Success Heralds Era Of Animal To Human Transplants Financial Times. In the uk, for example, you can now i don't know if it's india, or japan, or south america, or new york, but we want instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very you may hear the process of 3d printed organs described as 3d bioprinting, with the final products (organs) being called engineered organs. This is still not a reality. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters. A transparent human brain is shown by dr. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. The fear a person may feel when told he or she needs a new lung or kidney may soon by a thing of the past as medical science is quickly learning how to use 3d printing technology to build replacements. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down researchers hope that organ printing could decrease the organ transplant shortage.40 there is currently a shortage of available organs the new york times. We can see where every single cell is located. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope.
How 3 D Printing Is Changing Health Care Wsj - A New Review Looks At The Likelihood Of 3D Printed Organs And Analyzes Recent Accomplishments Their Research Paper Entitled Print Me An Organ!
Top 10 3d Printing Stories Of 2019. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. This is still not a reality. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very you may hear the process of 3d printed organs described as 3d bioprinting, with the final products (organs) being called engineered organs. We can see where every single cell is located. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. In the uk, for example, you can now i don't know if it's india, or japan, or south america, or new york, but we want instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down researchers hope that organ printing could decrease the organ transplant shortage.40 there is currently a shortage of available organs the new york times. The fear a person may feel when told he or she needs a new lung or kidney may soon by a thing of the past as medical science is quickly learning how to use 3d printing technology to build replacements. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time. A transparent human brain is shown by dr.
A Review On The 3d Printing Of Functional Structures For Medical Phantoms And Regenerated Tissue And Organ Applications Sciencedirect . Using A Natural Human Enzyme That Works In Water, Process Uses No Toxic.
Development Of 3d Bioprinting From Printing Methods To Biomedical Applications Sciencedirect. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters. We can see where every single cell is located. This is still not a reality. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down researchers hope that organ printing could decrease the organ transplant shortage.40 there is currently a shortage of available organs the new york times. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials. The fear a person may feel when told he or she needs a new lung or kidney may soon by a thing of the past as medical science is quickly learning how to use 3d printing technology to build replacements. In the uk, for example, you can now i don't know if it's india, or japan, or south america, or new york, but we want instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very you may hear the process of 3d printed organs described as 3d bioprinting, with the final products (organs) being called engineered organs. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. A transparent human brain is shown by dr.
Disruptive Breakthroughs In 3d Printing Daniel Burrus , Organ Twins, 3D Prints Made From Ct Scans, 3D Printed Parts Helping Doctors Train Or Do Complex Surgeries Is Something We Hear About All Of The Time.
Lego Inspired Bone And Soft Tissue Repair With Tiny 3d Printed Bricks Ohsu News. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very you may hear the process of 3d printed organs described as 3d bioprinting, with the final products (organs) being called engineered organs. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. The fear a person may feel when told he or she needs a new lung or kidney may soon by a thing of the past as medical science is quickly learning how to use 3d printing technology to build replacements. We can see where every single cell is located. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time. In the uk, for example, you can now i don't know if it's india, or japan, or south america, or new york, but we want instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down researchers hope that organ printing could decrease the organ transplant shortage.40 there is currently a shortage of available organs the new york times. This is still not a reality. A transparent human brain is shown by dr. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters.
Would You Eat A Steak Printed By Robots Bbc News : The Foundation For A Printed Organ Is Known As A Scaffold, Made Of Biodegradable Materials.
A 3d Print Out You Could Call Home The New York Times. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very you may hear the process of 3d printed organs described as 3d bioprinting, with the final products (organs) being called engineered organs. The fear a person may feel when told he or she needs a new lung or kidney may soon by a thing of the past as medical science is quickly learning how to use 3d printing technology to build replacements. A transparent human brain is shown by dr. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. This is still not a reality. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope. We can see where every single cell is located. In the uk, for example, you can now i don't know if it's india, or japan, or south america, or new york, but we want instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down researchers hope that organ printing could decrease the organ transplant shortage.40 there is currently a shortage of available organs the new york times. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials.
Development Of 3d Bioprinting From Printing Methods To Biomedical Applications Sciencedirect - We Can See Where Every Single Cell Is Located.
Custom Organs Printed To Order Nova Pbs. We can see where every single cell is located. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. A transparent human brain is shown by dr. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. This is still not a reality. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down researchers hope that organ printing could decrease the organ transplant shortage.40 there is currently a shortage of available organs the new york times. The fear a person may feel when told he or she needs a new lung or kidney may soon by a thing of the past as medical science is quickly learning how to use 3d printing technology to build replacements. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very you may hear the process of 3d printed organs described as 3d bioprinting, with the final products (organs) being called engineered organs. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters. In the uk, for example, you can now i don't know if it's india, or japan, or south america, or new york, but we want instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time.
30 Things Being 3d Printed Right Now And None Of Them Are Guns 3d Printing The Guardian : In The Uk, For Example, You Can Now I Don't Know If It's India, Or Japan, Or South America, Or New York, But We Want Instead Of Printing Layer Upon Layer Of Living Cells To Form A 3D Structure, Like A Conventional 3D Printer Would Do.
Transplanting Organs From Pigs To Humans Science Immunology. The first microscopes were invented in the sixteenth century, around the time of the invention of the telescope. In reality, printed organs are a long way away. The foundation for a printed organ is known as a scaffold, made of biodegradable materials. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. The fear a person may feel when told he or she needs a new lung or kidney may soon by a thing of the past as medical science is quickly learning how to use 3d printing technology to build replacements. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very you may hear the process of 3d printed organs described as 3d bioprinting, with the final products (organs) being called engineered organs. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down researchers hope that organ printing could decrease the organ transplant shortage.40 there is currently a shortage of available organs the new york times. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. In the uk, for example, you can now i don't know if it's india, or japan, or south america, or new york, but we want instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Ali ertuerk at his laboratory in munich, germany.reuters. This is the most exciting project i've worked on in a long time. We can see where every single cell is located. This is still not a reality. A transparent human brain is shown by dr.


