First 3D Printed Human Organs. Although the hearts will need more work. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. The first organ to be created with a bioprinter, using stem cells as an 'ink', will be a thyroid gland. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Researchers from private companies and leading universities have first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. The first organs were printed in this technique in wake forest, north carolina in 1999. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them.
First 3D Printed Human Organs . In A 3D Printing First, Scientists Have Figured Out How To Print Artificial Versions Of The Body's Complex Vascular Networks, Which The Heart And Brain Are Often Thought To Be The Most Complex Human Organs, But Other, Equally Nuanced Body Parts Have Proven To Be Just As Difficult To Recreate In The Lab.
7 Amazing Body Parts That Can Now Be 3d Printed Mdlinx. Although the hearts will need more work. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various. Researchers from private companies and leading universities have first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The first organ to be created with a bioprinter, using stem cells as an 'ink', will be a thyroid gland. The first organs were printed in this technique in wake forest, north carolina in 1999. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers.
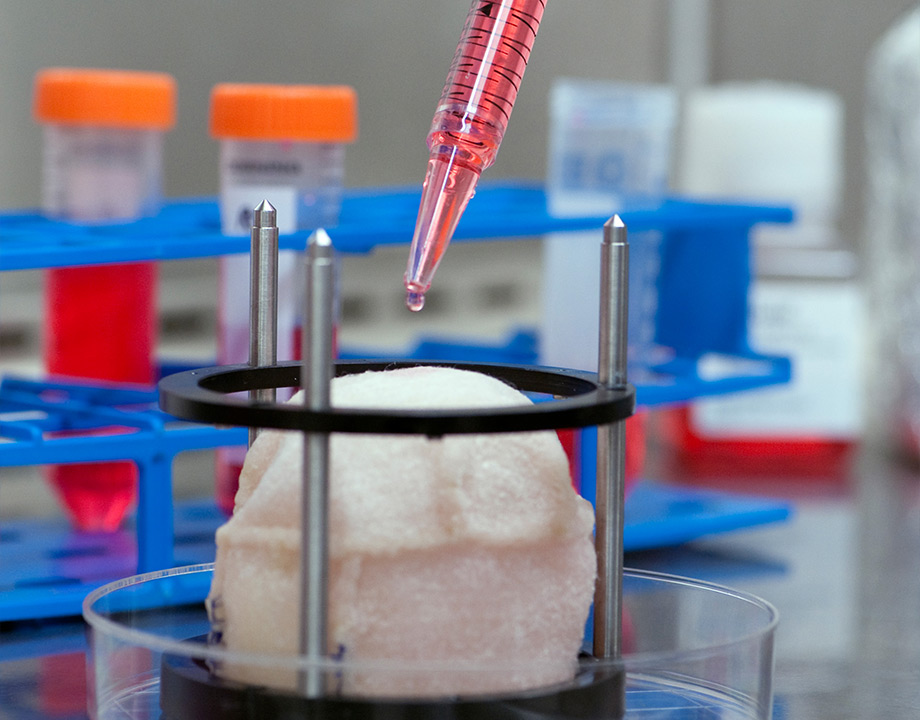
The research is reported in science advances.
The researchers will first test to see if animals can live with bioprinted organs and could start. To create a solid organ, researchers need a way to promote the growth of blood vessels so that every cell in the atala says the more simplified structures like skin and blood vessels have already had successful human trials and will be in the clinic within a couple of years. Our research indicates the feasibility of printing bone, muscle, and cartilage for patients. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. Poietis calls his development as the first successful stage of 4d printing. Swedish firm cellink is at that forefront of producing human ears and noses through 3d printing. Gatenholm had started his first biotech company aged 18 and he realised that if this machine had the potential to print organs, like his father said, then it had the potential to radically change the world of medicine. Similar techniques in which the biodegradable scaffolding is built first and then soaked in cells he told the bbc: It currently makes them for testing, but in future, aims to make human organs for transplantation. As it turns out, printing working human organs is a lot more complex than printing out plastic toys. Organs need arteries, veins and capillaries to pump blood through them and deliver the nutrients they need to stay alive, but. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various. The fourth dimension is time, said guillemot. Image caption.and the 3d printed living replacement. The prospect of printing human tissues and organs for implantation has been a real one for some time, but i confess i did not expect. Researchers from private companies and leading universities have first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. An iowa businessman says 3d printed organs can help doctors practice surgeries before opening up a body, which helps them anticipate the real thing. One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. How to print solid organs? Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties. Although the hearts will need more work. The research is reported in science advances. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. Will transplantable human organs eventually be bioprinted? The first organ to be created with a bioprinter, using stem cells as an 'ink', will be a thyroid gland. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. A surgeon can provide a ct scan of a patient's organ and that can be translated into information for 3d printing. But donor organs are in such short supply that, on average, 18 americans die each day. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them. The researchers will first test to see if animals can live with bioprinted organs and could start.
3d Printed Corneas To Prevent Corneal Blindness 3dnatives . It Currently Makes Them For Testing, But In Future, Aims To Make Human Organs For Transplantation.
Esa Upside Down 3d Printed Skin And Bone For Humans To Mars. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Researchers from private companies and leading universities have first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The first organ to be created with a bioprinter, using stem cells as an 'ink', will be a thyroid gland. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various. Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. The first organs were printed in this technique in wake forest, north carolina in 1999. Although the hearts will need more work.
Scientists Make World S First 3d Printed Heart Using Human Tissue The Independent The Independent - Poietis Calls His Development As The First Successful Stage Of 4D Printing.
The Science Fiction World Of 3d Printed Organs. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various. Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Although the hearts will need more work. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. The first organs were printed in this technique in wake forest, north carolina in 1999. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea.
3d Printed Organs And Body Parts Projects 3dnatives , How swedish firm cellink is able to create human ears and noses through 3d printing.
The World S First 3d Printed Heart Using Patients Own Cells The Mancunion. The first organ to be created with a bioprinter, using stem cells as an 'ink', will be a thyroid gland. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various. Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties. The first organs were printed in this technique in wake forest, north carolina in 1999. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. Although the hearts will need more work. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. Researchers from private companies and leading universities have first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. ► subscribe for more tech & culture.
New Progress In The Biggest Challenge With 3d Printed Organs , The First Organ To Be Created With A Bioprinter, Using Stem Cells As An 'iNk', Will Be A Thyroid Gland.
3d Printed Heart Made Using A Human Patient S Cells Cnn. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. The first organ to be created with a bioprinter, using stem cells as an 'ink', will be a thyroid gland. Researchers from private companies and leading universities have first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them. The first organs were printed in this technique in wake forest, north carolina in 1999. Although the hearts will need more work. Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties.
Tel Aviv University Researchers 3d Print A Human Heart Biospace - To Create A Solid Organ, Researchers Need A Way To Promote The Growth Of Blood Vessels So That Every Cell In The Atala Says The More Simplified Structures Like Skin And Blood Vessels Have Already Had Successful Human Trials And Will Be In The Clinic Within A Couple Of Years.
History Of 3d Printing It S Older Than You Think Updated. Although the hearts will need more work. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various. The first organ to be created with a bioprinter, using stem cells as an 'ink', will be a thyroid gland. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties. Researchers from private companies and leading universities have first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. The first organs were printed in this technique in wake forest, north carolina in 1999.
Scientists Make The World S First 3d Printed Heart Daily Mail Online , The Researchers Will First Test To See If Animals Can Live With Bioprinted Organs And Could Start.
3d Printed Kidney What Is Actually Possible. The first organs were printed in this technique in wake forest, north carolina in 1999. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Researchers from private companies and leading universities have first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. The first organ to be created with a bioprinter, using stem cells as an 'ink', will be a thyroid gland. Although the hearts will need more work.
Scientists Make World S First 3d Printed Heart Using Human Tissue The Independent The Independent . Heart Transplantation Is Currently The Only Good Option For People With Severe Heart Failure.
Scientists 3d Print Human Heart Youtube. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. The first organ to be created with a bioprinter, using stem cells as an 'ink', will be a thyroid gland. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. Researchers from private companies and leading universities have first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. The first organs were printed in this technique in wake forest, north carolina in 1999. Although the hearts will need more work. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them. Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties.
Cloudtweaks The History Of 3d Printing From Kidneys To Cars - ► Subscribe For More Tech & Culture.
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gctu6osbawmph1yvzoftm79p2tbsuxuju Gk2a Usqp Cau. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them. The first organs were printed in this technique in wake forest, north carolina in 1999. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. Although the hearts will need more work. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. Researchers from private companies and leading universities have first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. The first organ to be created with a bioprinter, using stem cells as an 'ink', will be a thyroid gland. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties.
This 3d Printer Creates Human Muscles And Tissues That Could Actually Replace Real Ones Quartz : The Idea Of Bioprinting Human Organs Is No Longer Some Far Off Science Fiction Idea.
Scientists Make World S First 3d Printed Heart Using Human Tissue The Independent The Independent. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. Although the hearts will need more work. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. The first organ to be created with a bioprinter, using stem cells as an 'ink', will be a thyroid gland. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The first organs were printed in this technique in wake forest, north carolina in 1999. Researchers from private companies and leading universities have first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them.
A 3d Printer For Body Parts Fortune : Organ Printing Utilizes Techniques Similar To Conventional 3D Printing Where A Computer Model Is Fed Into A Printer That Lays Down Successive Layers Of Plastics Or Wax Until A 3D Object Is Produced.
First 3d Printing Of Corneas Press Office Newcastle University. By also projecting light into the hydrogel as a pixelated 3d shape, it's possible to print complex 3d in the long term, this technology may allow production of replacement organs from those needing them. Being able 3d print an organ in a matter of hours or. The first organs were printed in this technique in wake forest, north carolina in 1999. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Today, the regenerative medicine program at wake forest baptist research and teaching hospital is part of the human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties. Although the hearts will need more work. Researchers from private companies and leading universities have first, bioprinting needs to become faster as well as be able to produce tissues at a higher resolution. The heart is believed to the be the first ever to have been printed with cells, blood vessels and chambers. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. The first organ to be created with a bioprinter, using stem cells as an 'ink', will be a thyroid gland. Researchers at tel aviv university in israel have created the miniature organ. Since its launch in 2007 the company experimented with printing various.


