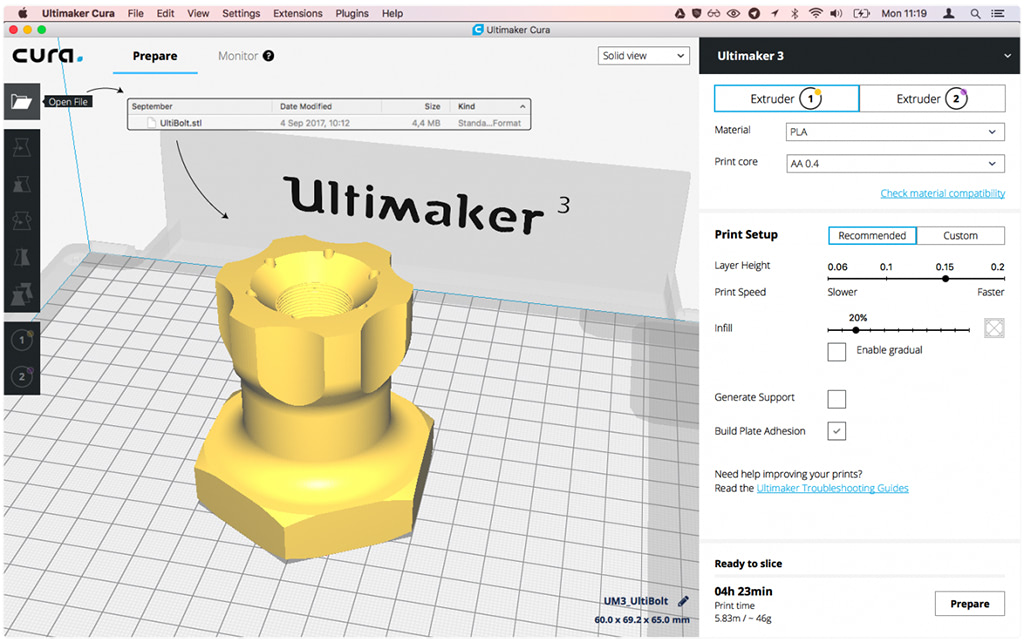
Limitations Of 3D Printing Organs. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics 3d printed organs could save people's lives. The stepwise process of printing a tissue, the limitations of current. 3d printing is also limited by the size of the 3d printer. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. What's the current status of 3d printed organs? Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be. Understanding of the composition and organization of their compo The bioprinter, of course, makes its way into the hands of lister and rimmer et al and goes on to exemplify both the hubris of humanity and the eternal limitations of tech. Technologies and the challenges for future research. Architecture of functional tissues and organs is a comprehensive. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research.
Limitations Of 3D Printing Organs : Recent Advances Have Enabled 3D Printing Of Biocompatible Materials, Cells And Supporting Components Into Complex 3D Functional Living Tissues.
Complex Formulations Simple Techniques Can 3d Printing Technology Be The Midas Touch In Pharmaceutical Industry Sciencedirect. The stepwise process of printing a tissue, the limitations of current. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. What's the current status of 3d printed organs? Architecture of functional tissues and organs is a comprehensive. The bioprinter, of course, makes its way into the hands of lister and rimmer et al and goes on to exemplify both the hubris of humanity and the eternal limitations of tech. Understanding of the composition and organization of their compo Technologies and the challenges for future research. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics 3d printed organs could save people's lives. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be. 3d printing is also limited by the size of the 3d printer.
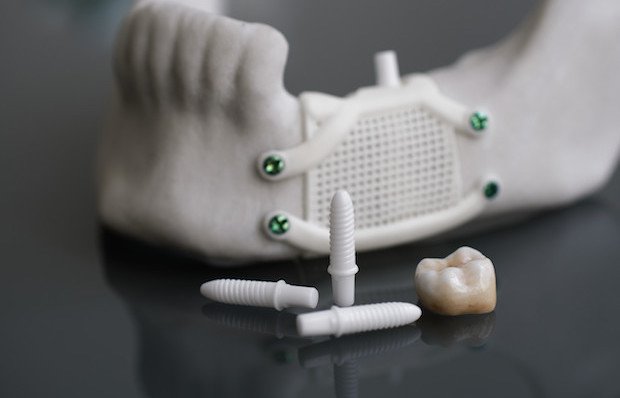
Would this cause ethical issues, allowing humans to take on.
3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Further, our organs actually contain independent vascular networks — like the airways and blood vessels of the lung or the bile ducts and blood vessels in the liver. Another organ she came up with is called the tremomucosa expulsum, and it is designed for people with cystic fibrosis. Three more prominent limitations of these techniques are the damages. Using bio printing, many companies and researchers have managed to make perfectly working body organs using a special ink made carefully from chemicals. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Tissue and organ printing is an emerging field that mainly focused on regenerative medicine and tissue engineering by both academy and industry (murphy common am techniques and printable materials are presented for better understanding of their potential, limitations, and applications. 3d bioprinting organs has led to major advances in drug screening, disease modeling and other areas. But prof atala said 3d printing. Would this cause ethical issues, allowing humans to take on. The production process is demonstrated by producing a set of eyeglass frames from 3d blueprints. Bioprinting has various limitations that lead to the development it is an ink formulation that dictates the printing of living cells. Will we one day soon be 3d printing organs which are unlike anything seen before in humans? Limitations of extrusion printing mean that technology is too low resolution and too slow to create capillaries and keep cells alive. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. The applications and limitations of 3d printing are discussed; But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. These 3d printing technologies have been defined as 3d bioprinting. Unlike normal printing, a 3d printer does not use ink or toner, but special types of materials. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be. What's the current status of 3d printed organs? First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. The difficulty of building organs with 3d printing falls into about four levels of complexity, atala said. Scientists are racing to make replacement human organs with 3d printers. Most bioprinters work by printing a kind of 3d gel known as a bioink, which comprises cells and a printable biomaterial like gelatin. Different machines do different things, with different goals and materials in mind, whether it is printing key chains and phone casings or printing out blood vessels and organs. These interpenetrating networks are physically and biochemically entangled, and the architecture itself is intimately related to tissue function. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics 3d printed organs could save people's lives. Not all surgical props are born equal, and there are often limitations as well as benefits to practicing on an artificial human, as they often don't accurately represent the behavior of their.
3d Bioprinting - Unlike Normal Printing, A 3D Printer Does Not Use Ink Or Toner, But Special Types Of Materials.
Frontiers 3d And 4d Printing Of Polymers For Tissue Engineering Applications Bioengineering And Biotechnology. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics 3d printed organs could save people's lives. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. The bioprinter, of course, makes its way into the hands of lister and rimmer et al and goes on to exemplify both the hubris of humanity and the eternal limitations of tech. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be. 3d printing is also limited by the size of the 3d printer. Understanding of the composition and organization of their compo 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Architecture of functional tissues and organs is a comprehensive. Technologies and the challenges for future research. The stepwise process of printing a tissue, the limitations of current. What's the current status of 3d printed organs?
Intro To 3d Bioprinting Design Applications And Limitations Lesson Teachengineering , Architecture Of Functional Tissues And Organs Is A Comprehensive.
3d Printing Dr Rajiv Desai. The stepwise process of printing a tissue, the limitations of current. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. What's the current status of 3d printed organs? Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be. The bioprinter, of course, makes its way into the hands of lister and rimmer et al and goes on to exemplify both the hubris of humanity and the eternal limitations of tech. Understanding of the composition and organization of their compo Technologies and the challenges for future research. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need.
Impact Of Three Dimensional Printing In Urology State Of The Art And Future Perspectives A Systematic Review By Esut Yauwp Group European Urology . Others even believe they'll be an improvement on the human machinery, but there are limitations.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Skin Bioprinting Download Scientific Diagram. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics 3d printed organs could save people's lives. Understanding of the composition and organization of their compo Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printing is also limited by the size of the 3d printer. Architecture of functional tissues and organs is a comprehensive. What's the current status of 3d printed organs? A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. The bioprinter, of course, makes its way into the hands of lister and rimmer et al and goes on to exemplify both the hubris of humanity and the eternal limitations of tech. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be. Technologies and the challenges for future research. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. The stepwise process of printing a tissue, the limitations of current. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer.
3d Printing . The Applications And Limitations Of 3D Printing Are Discussed;
3d Printing Medical Devices Market Global Forecast To 2022 By Technology Component Product Type. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics 3d printed organs could save people's lives. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be. 3d printing is also limited by the size of the 3d printer. The stepwise process of printing a tissue, the limitations of current. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The bioprinter, of course, makes its way into the hands of lister and rimmer et al and goes on to exemplify both the hubris of humanity and the eternal limitations of tech. Understanding of the composition and organization of their compo What's the current status of 3d printed organs? Architecture of functional tissues and organs is a comprehensive. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Technologies and the challenges for future research.
Everything You Need To Know About 3d Printing Ultimate Guide 2019 , But While The Technology's Possibilities Are Exciting, Already There Are Fears We The Most Promising Method Could Prove To Be Bioprinted Cell Scaffolds.
Implantable 3d Printed Organs Could Be Coming Sooner Than You Think Techcrunch. The bioprinter, of course, makes its way into the hands of lister and rimmer et al and goes on to exemplify both the hubris of humanity and the eternal limitations of tech. Architecture of functional tissues and organs is a comprehensive. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics 3d printed organs could save people's lives. Technologies and the challenges for future research. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. What's the current status of 3d printed organs? Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The stepwise process of printing a tissue, the limitations of current. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. 3d printing is also limited by the size of the 3d printer. Understanding of the composition and organization of their compo A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research.
3d Printed Kidneys Take Small Steps Toward Organ Replacements Live Science , But While The Technology's Possibilities Are Exciting, Already There Are Fears We The Most Promising Method Could Prove To Be Bioprinted Cell Scaffolds.
What Are The Disadvantages Of 3d Printing Inkjet Wholesale Blog. What's the current status of 3d printed organs? Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. The stepwise process of printing a tissue, the limitations of current. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; 3d printing is also limited by the size of the 3d printer. Understanding of the composition and organization of their compo The bioprinter, of course, makes its way into the hands of lister and rimmer et al and goes on to exemplify both the hubris of humanity and the eternal limitations of tech. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. Architecture of functional tissues and organs is a comprehensive. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. Technologies and the challenges for future research. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics 3d printed organs could save people's lives. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be.
Implantable 3d Printed Organs Could Be Coming Sooner Than You Think Techcrunch - Further, Our Organs Actually Contain Independent Vascular Networks — Like The Airways And Blood Vessels Of The Lung Or The Bile Ducts And Blood Vessels In The Liver.
3d Bio Printing Becoming Economically Feasible. The stepwise process of printing a tissue, the limitations of current. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Architecture of functional tissues and organs is a comprehensive. What's the current status of 3d printed organs? 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics 3d printed organs could save people's lives. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. The bioprinter, of course, makes its way into the hands of lister and rimmer et al and goes on to exemplify both the hubris of humanity and the eternal limitations of tech. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be. Understanding of the composition and organization of their compo 3d printing is also limited by the size of the 3d printer. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. Technologies and the challenges for future research. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced.
3d Bioprinting , Architecture Of Functional Tissues And Organs Is A Comprehensive.
Multi Material 3d And 4d Printing A Survey Rafiee 2020 Advanced Science Wiley Online Library. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; 3d printing is also limited by the size of the 3d printer. Technologies and the challenges for future research. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics 3d printed organs could save people's lives. The bioprinter, of course, makes its way into the hands of lister and rimmer et al and goes on to exemplify both the hubris of humanity and the eternal limitations of tech. The stepwise process of printing a tissue, the limitations of current. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Architecture of functional tissues and organs is a comprehensive. Understanding of the composition and organization of their compo Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be. What's the current status of 3d printed organs? Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced.
Israelis Create World S First 3d Printed Heart With Blood Vessels Israel21c - Tissue And Organ Printing Is An Emerging Field That Mainly Focused On Regenerative Medicine And Tissue Engineering By Both Academy And Industry (Murphy Common Am Techniques And Printable Materials Are Presented For Better Understanding Of Their Potential, Limitations, And Applications.
Malaysia Researchers Provide Overview Of Challenges In 3d Printing Biomedical Products 3dprint Com The Voice Of 3d Printing Additive Manufacturing. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. The stepwise process of printing a tissue, the limitations of current. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. What's the current status of 3d printed organs? Understanding of the composition and organization of their compo First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics 3d printed organs could save people's lives. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be. The bioprinter, of course, makes its way into the hands of lister and rimmer et al and goes on to exemplify both the hubris of humanity and the eternal limitations of tech. Architecture of functional tissues and organs is a comprehensive. 3d printing is also limited by the size of the 3d printer. Technologies and the challenges for future research.
Rapid 3d Printing Of High Res Viable Human Organs Possible Evolving Science : The Bioprinter, Of Course, Makes Its Way Into The Hands Of Lister And Rimmer Et Al And Goes On To Exemplify Both The Hubris Of Humanity And The Eternal Limitations Of Tech.
Impact Of Three Dimensional Printing In Urology State Of The Art And Future Perspectives A Systematic Review By Esut Yauwp Group European Urology. Technologies and the challenges for future research. Architecture of functional tissues and organs is a comprehensive. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. What's the current status of 3d printed organs? First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that operates as a scaffold material; The stepwise process of printing a tissue, the limitations of current. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printing holds the promise of changing the healthcare industry for the better, offering patients things like smarter drugs, hyper customized prosthetics 3d printed organs could save people's lives. 3d printing is also limited by the size of the 3d printer. Understanding of the composition and organization of their compo 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare. A new review looks at the likelihood of 3d printed organs and analyzes recent accomplishments, limitations and opportunities for future research. Due to the tremendous demand for organs, it has been estimated that 900,000 deaths each year could be. The bioprinter, of course, makes its way into the hands of lister and rimmer et al and goes on to exemplify both the hubris of humanity and the eternal limitations of tech. Like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer.